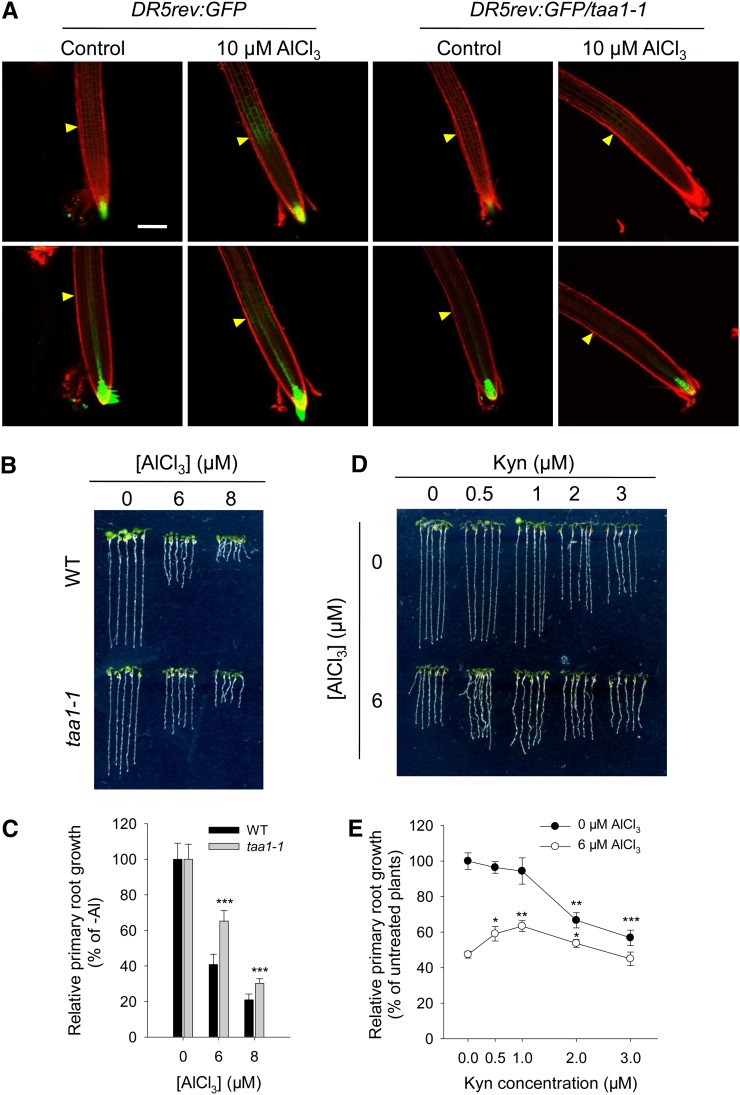
Figure 3.
Both Auxin Signaling Maximum in the TZ and Al-Induced Inhibition of Root Growth Are Regulated by TAA1.
(A) Expression of the DR5rev:GFP transgene in the root tip of the wild type and the loss-of-function mutant taa1-1. Six-day-old DR5rev:GFP and DR5rev:GFP/taa1-1 seedlings were exposed for 2 h to either 0 (control) or 10 μM AlCl3. The top row shows DR5rev:GFP signals in the epidermis, and the bottom row shows DR5rev:GFP signals in the cortex. Cell boundaries appear red following PI staining. The TZ is marked by yellow arrowheads. Bar = 100 μm.
(B) and (C) Root growth of wild-type and taa1-1 plants after a 7-d exposure to 0, 6, or 8 μM AlCl3. Asterisks in (C) indicate that means within the wild type and the taa1-1 mutant in each Al concentration differ significantly at ***P < 0.001 (t test).
(D) and (E) Effect on the Al-induced inhibition of root growth of adding the TAA1 inhibitor Kyn. Root growth was measured after a 7-d exposure to 0 or 6 μM AlCl3 in the presence of 0 to 3 μM Kyn. Asterisks in (E) indicate that Kyn treatments differ significantly at *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 (t test).
Values in (C) and (E) represent means ± sd (n = 30).