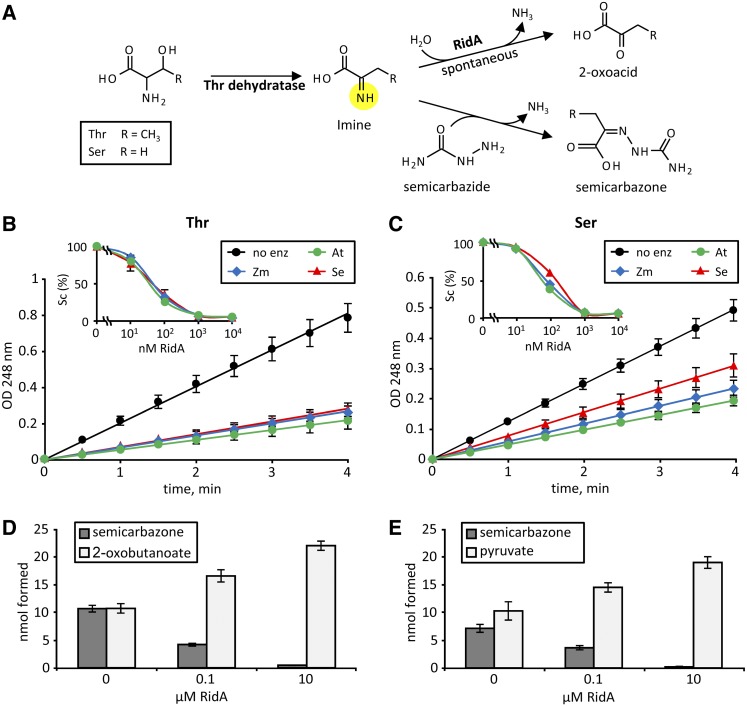
Figure 3.
Plant RidA Proteins Accelerate the Rate of Hydrolysis Thr- and Ser-Derived Reactive Imines Produced by Arabidopsis Thr Dehydratase.
(A) The imines produced by Thr dehydratase can be hydrolyzed to the corresponding 2-oxoacids spontaneously or via RidA action. Alternatively, the imines can react with semicarbazide to produce semicarbazones that absorb strongly at 248 nm.
(B) and (C) Plant RidA proteins accelerate hydrolysis of Thr- and Ser-derived imine intermediates, respectively. Assays contained 100 nM Arabidopsis (At), maize (Zm), or S. enterica (Se) RidA, 0.5 μM (Thr) or 2.5 μM (Ser) Arabidopsis Thr dehydratase, 10 mM semicarbazide, and were started by addition of Thr or Ser (final concentration 2 mM). Insets show the rate of semicarbazone (Sc) formation in assays containing various concentrations of RidA, expressed as a percentage of that in reactions without RidA. Data are means and se for three independent assays. Where no error bars are shown they were smaller than the symbols.
(D) and (E) The RidA-mediated reduction in semicarbazone formation is accompanied by an increase in 2-oxoacid formation from Thr or Ser, respectively. Arabidopsis RidA was used; reaction time was 5 min. Data are means and se for three independent assays.