Figure 3.
GNOM-GFP Localizes Primarily to the Golgi Apparatus.
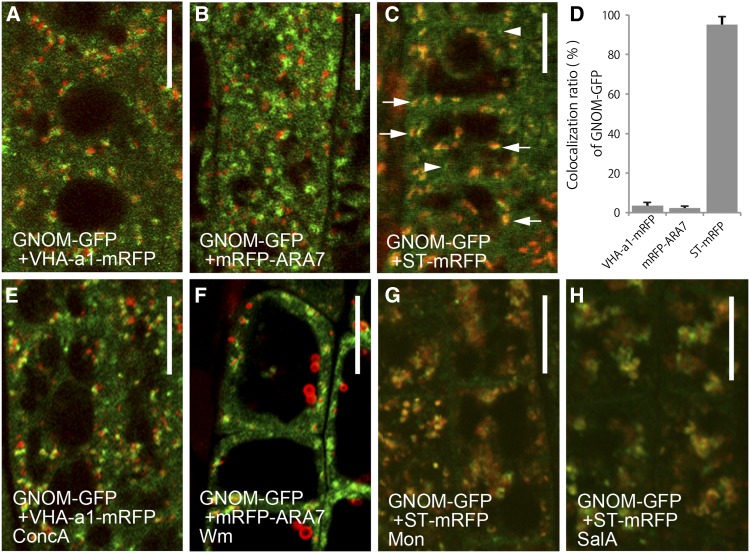
(A) to (D) Double labeling of GNOM-GFP (green) and subcellular markers tagged with RFP (red) in normal conditions. Compared with VHA-a1-mRFP (A) and mRFP-ARA7 (B), GNOM-GFP localizes to distinct compartments. GNOM-GFP colocalizes with the Golgi marker, ST-mRFP (C). The colocalization percentage is shown in (D). Arrows and arrowheads indicate ST-mRFP-positive and -negative GNOM-GFP-labeled compartments, respectively. Error bars indicate the sd values for data from three independent experiments. At least 200 GNOM-GFP-labeled organelles were analyzed in each experiment.
(E) to (H) Response of GNOM-GFP and RFP-tagged organelle markers to pharmacological interference. Root cells expressing GNOM-GFP treated with ConcA (E), Wm (F), monensin (Mon) (G), and salinomycin A (SalA) (H). For testing the effectiveness of chemicals, VHA-a1-mRFP (E), mRFP-ARA7 (F), and ST-mRFP ([G] and [H]) were used as a control. Treatment with Mon and SalA was performed for 30 min; treatment with ConcA and Wm was performed for 1 h. The distribution of GNOM-GFP changes after Mon and SalA treatments.
Bars = 8 µm.