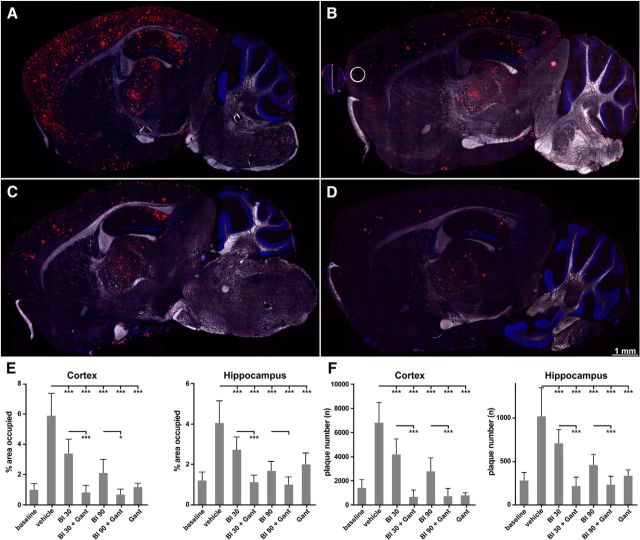
Figure 4.
Efficacy of mono- and combination treatments on brain amyloid burden and plaque number. Animals were treated with BACE inhibitor RO5508887 at either 30 or 90 mg/kg daily (BI30, BI90), with anti-Aβ antibody gantenerumab (Gant) at 20 mg/kg weekly or with both compounds (BI30+Gant, BI90+Gant). A–D, Fluorescence images of entire sagittal brain sections after staining of amyloid plaques at study end. Representative images are shown after vehicle-treatment (A), treatment with BI90 (B), gantenerumab (C), and gantenerumab combined with BI90 (D). Notably, plaque reduction is most substantial in the animals that received both drugs. E, The quantification and statistical evaluation of the area surface occupied by plaques across all treatment groups for cortex and hippocampus. Decrease of plaque surface is significant while variable in treatment groups compared with vehicle-treated mice. The combination treatment significantly enhances the amyloid-plaque lowering for both the low- and the high-dose of RO5508887 in the cortex. F, Effect of mono- and combination treatments on total plaque number. Significantly enhanced efficacy by combination treatment is seen in both brain regions examined. Bars represent the mean of 10–4 animals (+SD).