Fig. 3.
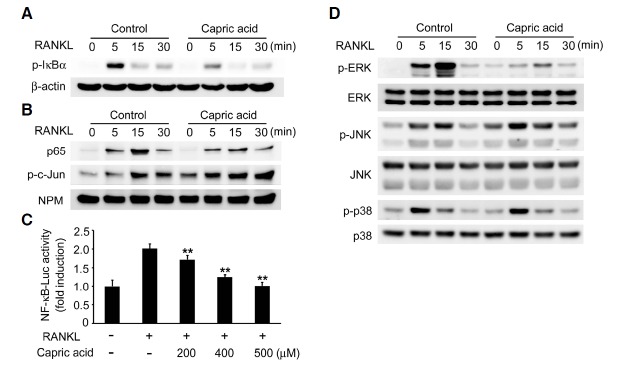
Effect of capric acid on RANKL-mediated signaling. (A) BMMs were pretreated with capric acid (500 μM) or vehicle for 2 h and then stimulated by the addition of RANKL (50 ng/ml) for the indicated time. Total cell lysates were immunoblotted with an anti-phospho-IκBα antibody. β-Actin served as a loading control. (B) The nuclear levels of p65 and phospho-c-Jun in the nuclear extracts of BMMs, as described in (A), were determined by immunoblotting. (C) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with an NF-κB reporter luciferase plasmid. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were pretreated with the indicated concentration of capric acid and then stimulated with RANKL (200 ng/ml). After 24 h, the cells were lysed, and the luciferase activity was determined. The data are expressed as the means ± SD. **P < 0.001 versus RANKL alone. (D) Cells were prepared as in (A) and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. The total ERK, JNK, and p38 levels served as loading controls.
