Fig. 4.
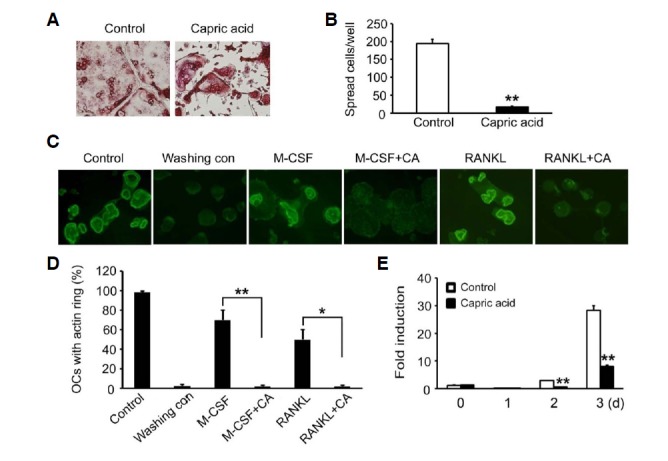
Effect of capric acid on organization of osteoclast cytoskeleton. (A, B) BMMs were cultured in an osteoclastogenic medium containing MCSF (10 ng/ml) and RANKL (20 ng/ml) for 3 days. The cells were then treated with capric acid or vehicle for 16 h. (A) The cells were fixed and stained for TRAP. (B) The number of spreading TRAP-positive cells was counted. The data are expressed as the means ± SD. **P < 0.001. (C, D) Mature osteoclasts cultured on bone slices were washed with cytokine-free cold media (Washing control) to disrupt the actin rings. The cells were then incubated without or with capric acid (400 μM) in the presence of M-CSF (50 ng/ml) or RANKL (20 ng/ml). (C) After 3 h of incubation, the cells were fixed and stained with FITC-phalloidin. (D) The percentage of osteoclasts with an actin ring was determined. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001. (E) BMMs were cultured with M-CSF and RANKL for the indicated number of days in the presence or absence of capric acid. β3 integrin expression was analyzed by real-time PCR. **P < 0.001 versus vehicle-treated control.
