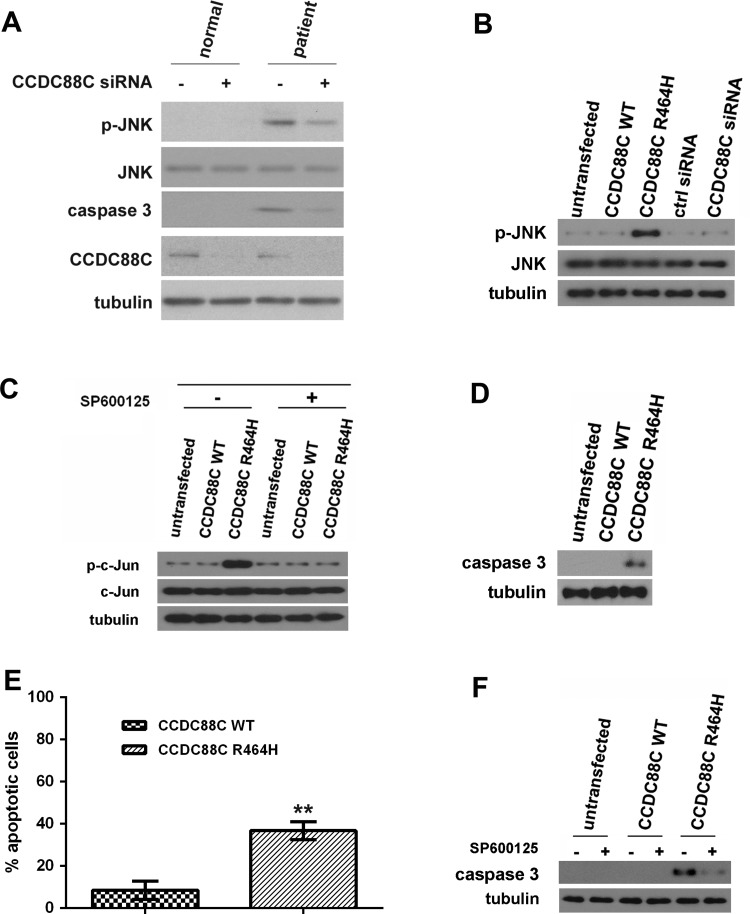
Figure 2.
Coiled-coil domain containing 88C (CCDC88C) protein carrying the R464H mutation activated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and caspase 3 apoptotic pathways. (A) Increased level of phosphorylated JNK was detected in patient primary fibroblasts (II:5) but not in that isolated from the unaffected sibling (II:7). Skin fibroblasts were isolated and cultured as described.31 Fibroblasts were treated with 5 pmol of ON-TARGETplus (Dharmacon) CCDC88C siRNA L-033364-00-0005 (+) or control (ctrl) siRNA (−). Total and phospho-JNK proteins were detected using anti-JNK 3708 (1:1 000, Cell Signaling Technology) and anti-p-JNK 5136 (1:1 000; Cell Signaling Technology) antibodies, respectively. Cleaved caspase 3 was detected by an antiactivated caspase 3 antibody Asp175 (1:5 00; Cell Signaling Technology). Endogenous CCDC88C was detected by anti-CCDC88C antibody A302-951A (1:1 000; Bethyl Laboratories). The experiment was repeated for at least three times. Only representative blots are shown. (B) Overexpression of mutant (MT) CCDC88C protein led to hyperphosphorylation of JNK in HEK293 cells. Both WT and MT CCDC88C expression constructs (0.5 µg) were used to transfect HEK293 cells. Cells were harvested 24 h after transfection. To knockdown CCDC88C expression, cells were treated with 5 pmol of ON-TARGETplus CCDC88C siRNA L-033364-00-0005 (Dharmacon) or control (ctrl) siRNA (Dharmacon). Cell lysates were analysed by western blotting with anti-JNK 3708 (1:1 000, Cell Signaling Technology) and anti-p-JNK 5136 (1:1 000; Cell Signaling Technology) antibodies. Neither the knockdown of CCDC88C WT expression nor its overexpression altered the level of JNK phosphorylation. The experiment was repeated for at least three times. Only representative blots are shown. (C) Phosphorylation of c-Jun was detected in HEK293 cells transiently expressing the CCDC88C MT protein. For JNK inhibitor treatment, cells were treated with 25 µM of SP600125 (Sigma) for 24 h. ‘+’ and ‘−’ denote cells with and without SP600125 treatment, respectively. Cell lysates were analysed by western blotting with anti-c-Jun 2315 (1:1 000, Cell Signaling Technology) and anti-p-c-Jun 9164 (1:1 000; Cell Signaling Technology) antibodies. The experiment was repeated for at least three times. Only representative blots are shown. (D) Overexpression of MT CCDC88C protein-induced caspase 3 activation in HEK293 cells. Cell lysates were analysed by western blotting and detected using an antiactivated caspase 3 antibody Asp175 (1:500; Cell Signaling Technology). The experiment was repeated for at least three times. Only representative blots are shown. (E) Overexpression of MT CCDC88C protein-induced apoptosis in HEK293 cells. Apoptosis was detected using the APO-BrdU TUNEL Assay Kit, with Alexa Fluor 488 Anti-BrdU (Life Technologies). The data represent means ±SD from four independent experiments. At least 100 cells were counted in each experiment. **denotes p<0.005. (F) Caspase 3 activation induced by MT CCDC88C protein expression can be blocked by JNK inhibitor. ‘+’ and ‘−’ denote cells with and without SP600125 treatment, respectively. The experiment was repeated for at least three times. Only representative blots are shown. Tubulin was used as loading control in all experiments and was detected using anti-β tubulin antibody E7 (1:10 000; Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank).