Abstract
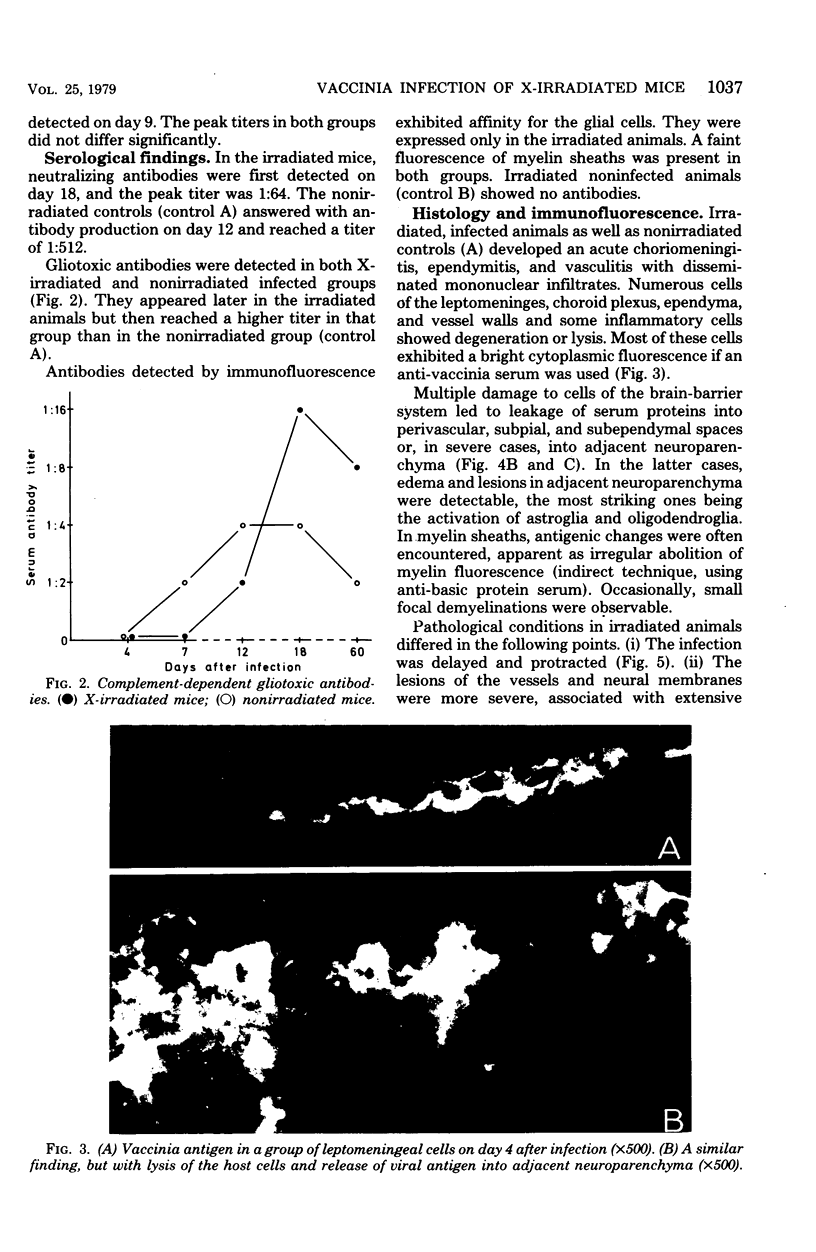
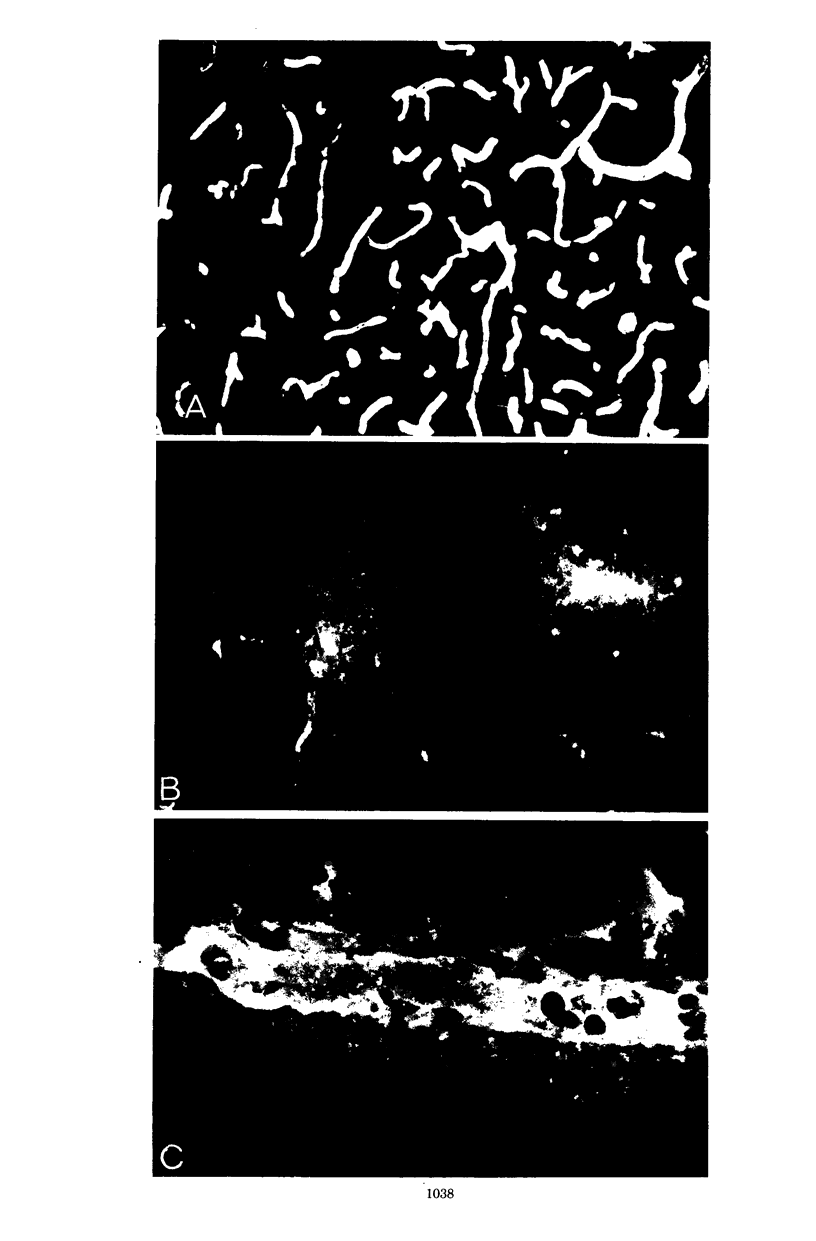
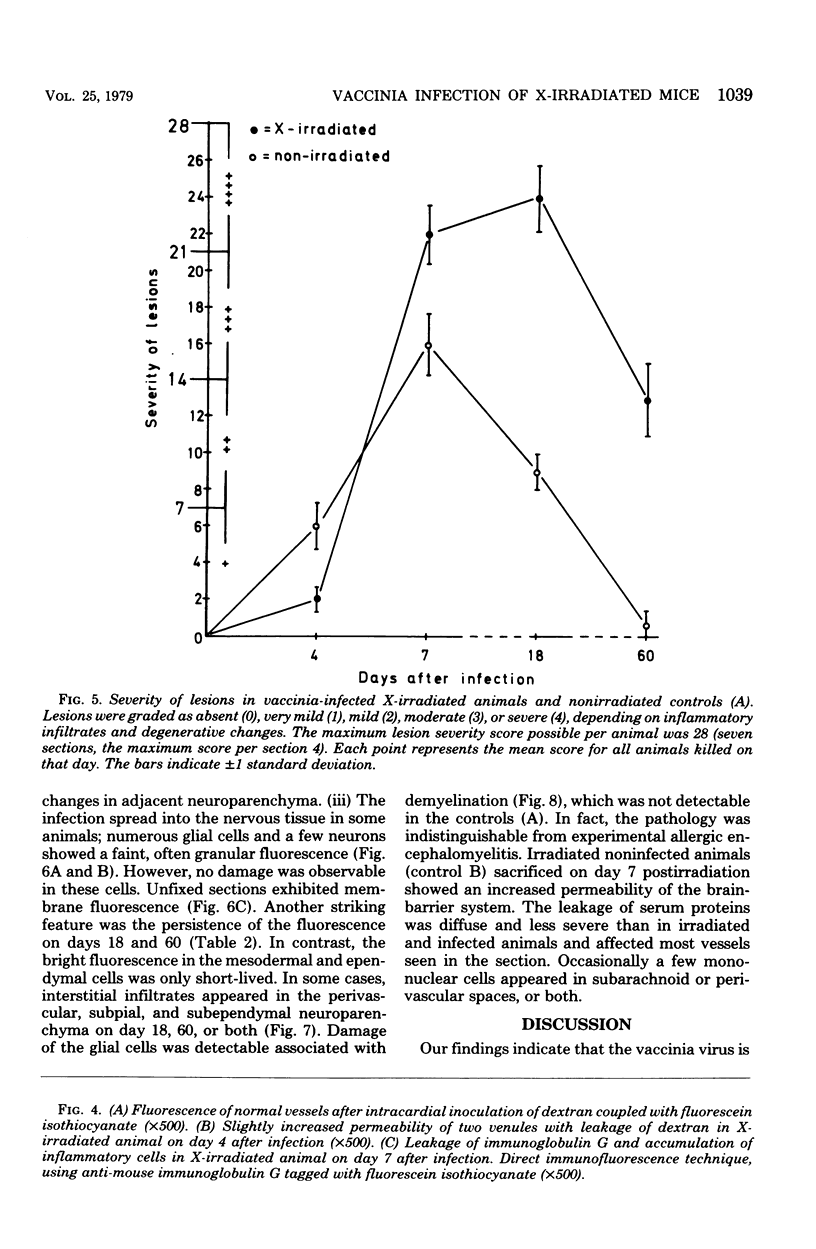
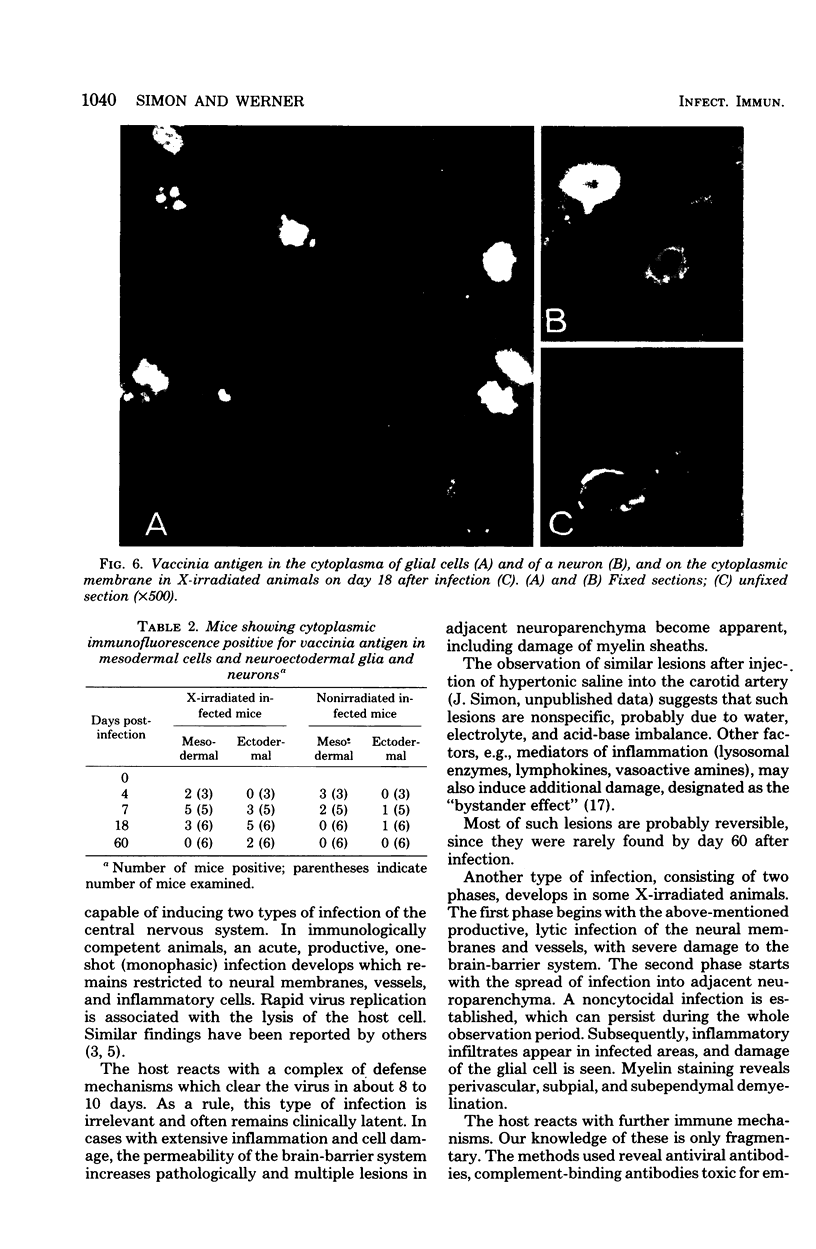
The effect of X-irradiation on experimental vaccinia infection of BALB/c mice was studied. As compared with nonirradiated controls, the X-irradiated animals exhibited (i) a time lag in virus replication (delayed, but protracted replication); (ii) a delayed and repressed immune response: (iii) more severe acute cytocidal infection of leptomeninges, choroid plexus, ependyma, and vessels, with extensive damage to the brain-barrier system; and (iv) noncytocidal, latent infection of glial cells and neurons. Several animals developed acute or subacute demyelination disease, resembling experimental allergic encephalomyelitis or postinfectious encephalomyelitis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandlow G., Fischer W., Thomssen R. Untersuchungen zum Mechanismus der immunologischen Adjuvanswirkung des Vacciniavirus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;38(2):192–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandlow G., Koszinowski U., Thomssen R. Gesteigerte Immunogenität von Plasmamembranen vacciniavirusinfizierter BHK-Zellen. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;40(1):63–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinzinger K., Hochstein-Mintzel V., Anzil A. P. Experimental vaccinia virus meningoencephalitis in adult albino mice: virological, light microscopic and ultrastructural studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Nov 28;40(3):193–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00691954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg A. H., Johnson K. P. Vaccinia virus meningitis in mice after intracerebral inoculation. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1221–1227. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1221-1227.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter D. H., Choppin P. W. Possible mechanisms in the pathogenesis of "postinfectious" encephalomyelitis. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1971;49:342–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L., Mergenhagen S. E., Howard R. J. Effect of virus infections on the function of the immune system. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:525–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J., Anzil A. P. Immunohistological evidence of perivascular localization of basic protein in early development of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol. 1974 Feb 7;27(1):33–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00687238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J., Hochstein-Mintzel V., Huber H. C., Gradl A., Hansert E. Die Suppression der experimentellen allergischen Encephalomyelitis durch vaccinia-virus-induzierte Hirnantikörper. Z Immunitatsforsch Immunobiol. 1977 Apr;153(1):23–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J., Hochstein-Mintzel V., Huber H. C., Zinn K. H., Stickl H. Sensibilisierung gegen Antigene des Zentralnervensystems nach experimenteller Infektion mit Vaccinia-Virus. II. Nachweis einer humoralen Sensibilisierung: pathomorphologische und immunhistologische Veränderungen im ZNS. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975 Jun;232(1):8–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarro G., Sabin A. B. Increase in preexisting cellular antigen-combining groups at different times after infection with different viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):731–737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda Y., Ito M., Tagaya I. A specific surface antigen induced by poxvirus. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):180–182. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]