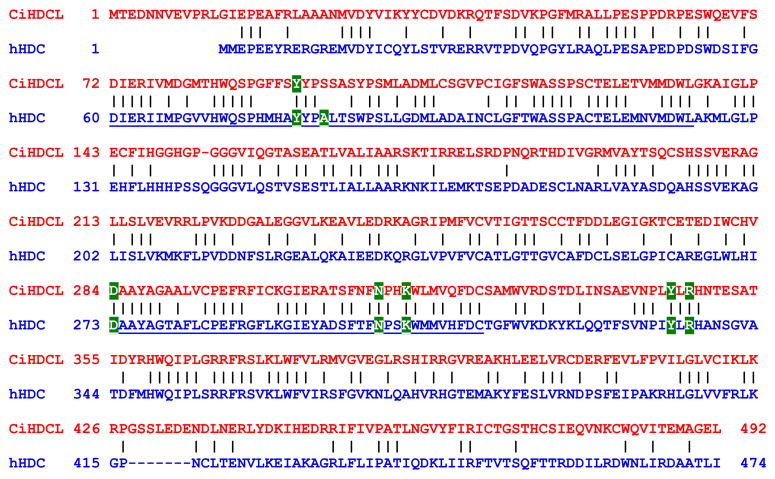
Fig. 2.
Isolation and characterization of a C. intestinalis transcript that encodes a HDC-like protein. A C. intestinalis cDNA was isolated (see GenBank accession number EF125183) that encoded a novel 492-mer protein that was ~50% identical to residues 1-474 of human histidine decarboxylase (hHDC). Additional information on this cDNA (accession number cidg826g09) can be found at http://ghost.zool.kyoto-u.ac.jp/. Shown is a comparison of the C. intestinalis HDC-like protein (CiHDCL) and hHDC. Using an expression/site-directed mutagenesis approach, two regions (corresponding to underlined residues 60-123 and 273-313 in hHDC) and seven amino acids (i.e., Y80, A83, D273, N302, K305, Y334, and R336) have been identified in hHDC that are important for the enzymatic activity of this decarboxylase. CiHDCL possesses those regions as well as the amino acids that are essential for histamine biosynthesis. hHDC is abundant in the gastric mucosa of humans as well as their tissue MCs. The fact that the CiHDCL cDNA was isolated from the sea squirt’s digestive gland is further evidence that it is the likely ortholog of hHDC. Only one CiHDCL EST was present in our library of ~600,000 C. intestinalis ESTs. Thus, CiHDCL is a highly restricted transcript in C. intestinalis as is HDC in humans.