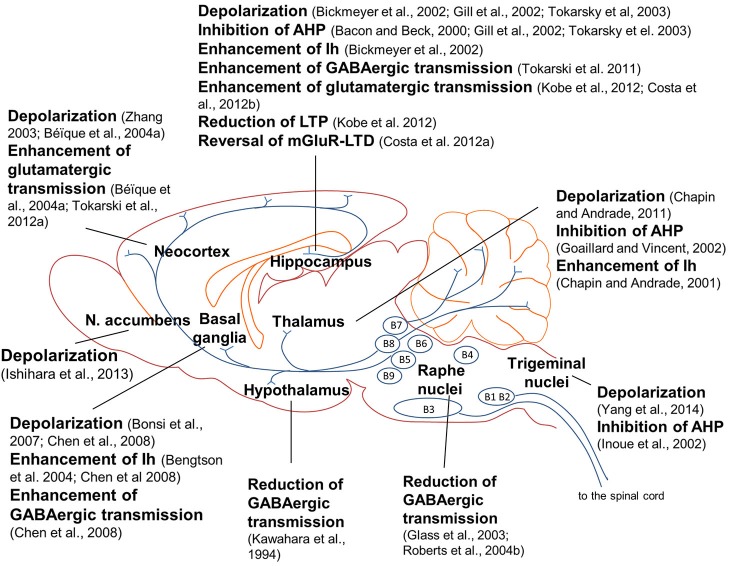
Figure 1.
Effects of 5-HT7 receptor activation on neuronal excitability, synaptic transmission and synaptic plasticity in the rodent brain. Activation of 5-HT7 receptors induced depolarization in several brain regions; in many cases, depolarization was mediated by inhibition of a post-spike afterhyperpolarization (AHP) and/or enhancement of a hyperpolatization-activated cation current (Ih; see explanations in the text). Activation of 5-HT7 receptors modulated glutamate-mediated synaptic transmission and plasticity in frontal cortex and hippocampus. 5-HT7 receptors differently modulated GABAergic synaptic transmission in distinct brain areas; notably, activation of 5-HT7 receptors in raphe nuclei inhibited GABAergic interneurons, enhancing the activity of serotonergic raphe neurons and 5-HT release in target structures. Most of the results illustrated here were obtained in the rat, with the following exceptions: mouse (Bickmeyer et al., 2002; Costa et al., 2012a; Yang et al., 2014), hamster (Glass et al., 2003) and guinea pig (Roberts et al., 2004b).