Figure 2.
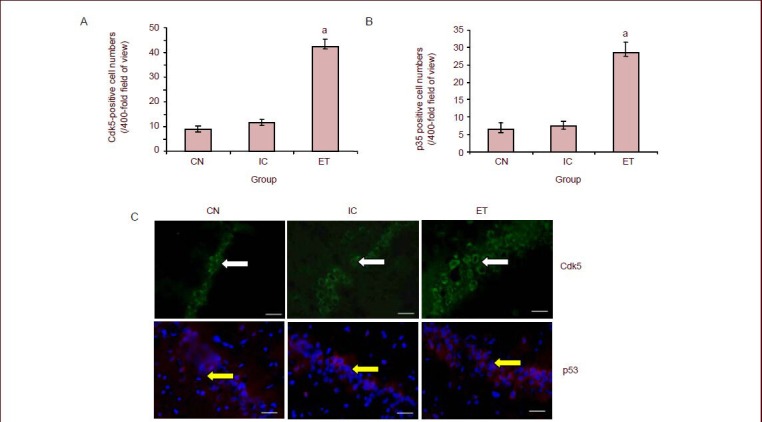
Effects of maternal alcohol consumption on cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) and p35 expression in the hippocampus of rat offspring (immunofluorescence, × 400).
(A, B) Bar graph of Cdk5- and p35-positive cell numbers in the hippocampus. aP < 0.01, vs. CN and IC. Data are expressed as mean ± SD,n= 18 rats in each group. The experiment was repeated three times, and analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and the least significant difference multiple-range test.
(C) Representative photomicrographs of Cdk5 (Alexa Fluor 488-labeled, green fluorescence) and p35 (Cy3-labeled, red fluorescence) with immunofluorescent staining in the rat hippocampus. Scale bars: 10 μm. Cells with Cdk5 expression are green (white arrows). In contrast, cells with p35 expression are red (yellow arrows). Compared with the control and isocaloric groups, a large number of hippocampal neurons were stained with fluorescence in the offspring from the ethanol-treated group, and the density and fluorescence intensity increased.
CN: Control group; ET: ethanol-treated group; IC: isocaloric group.
