Figure 2.
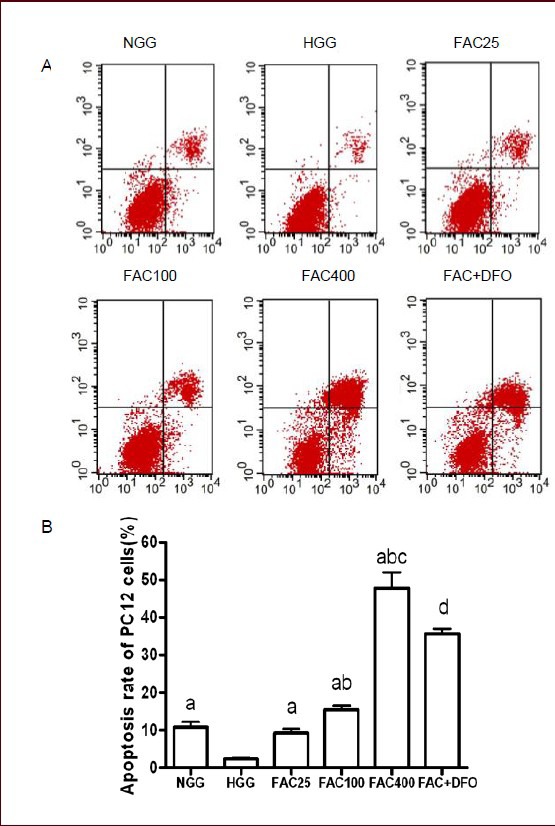
Apoptosis rate was increased by ferric ammonium citrate (FAC) and decreased by deferoxamine (DFO) in PC12 cells after 48 hours of culture (annexin V-FITC/PI staining and flow cytometry).
(A) Apoptosis rate of PC12 cells in the six groups was measured by annexin V-FITC/PI staining and flow cytometry. X-axis: The number of cells positive for annexin V-FITC staining; Y-axis: the number of propidium iodide-stained cells. First quadrant: Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide double-stained cells, representing late apoptotic cells. Second quadrant: Annexin V-FITC-negative and propidium iodide-positive cells, representing necrotic cells. Third quadrant: Annexin V-FITC-negative and propidium iodide-negative cells, representing normal cells. Fourth quadrant: Annexin V-FITC-positive and propidium iodide-negative cells, representing early apoptotic cells. (B) A histogram of the apoptosis rate of PC12 cells in the different groups. FAC increased apoptosis rate in a concentration-dependant manner. DFO rescued the neurotoxicity caused by FAC.
Data are shown as mean ± SD from triplicate experiments. One-way analysis of variance was adopted for multiple-group comparison. Two-tailed Student's t-test was used for intergroup comparison. aP < 0.05, vs. HGG; bP < 0.01, vs. 25 μmol/L FAC group; cP < 0.01, vs. 100 μmol/L FAC group; dP < 0.01, vs. 400 μmol/L FAC group.
NGG: Normal glucose concentration group; HGG: high glucose concentration group; FAC25: 25 μmol/L FAC group; FAC100: 100 μmol/L FAC group; FAC400: 400 μmol/L FAC group; FAC + DFO: 400 μmol/L FAC + 200 μmol/L DFO group.
