Figure 3.
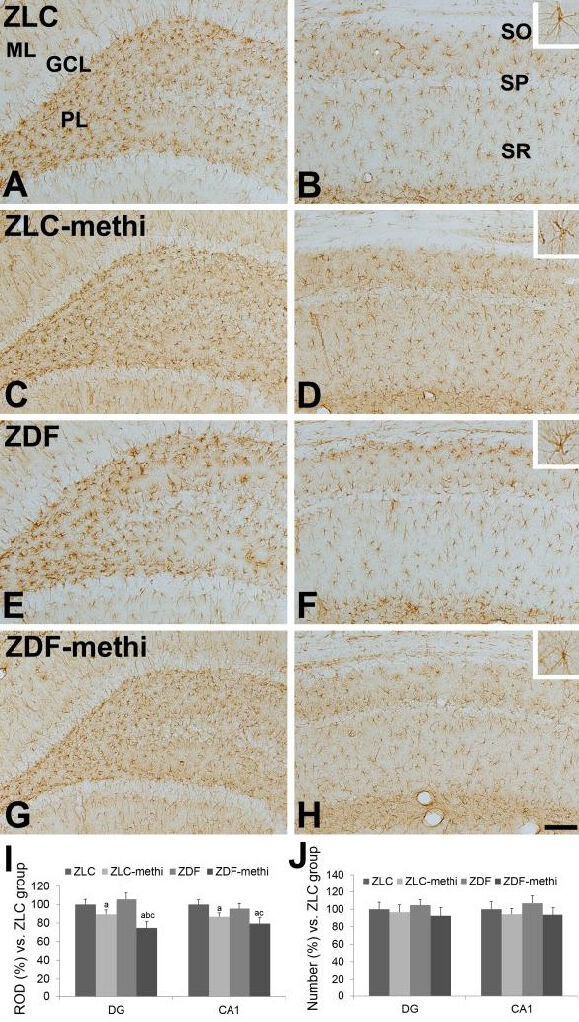
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunoreactivity in the dentate gyrus (A, C, E, and G), and CA1 region (B, D, F, and H) of vehicle-treated Zucker lean control (ZLC; A, B), methimazole-treated ZLC (ZLC-methi; C, D), vehicle-treated Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF; E, F), and methimazole-treated ZDF (ZDF-methi; G, H) rats.
GFAP immunoreactivity is mainly detected in the polymorphic layer (PL) and molecular layer (ML) of the dentate gyrus and stratum oriens (SO) and radiatum (SR) of CA1 region. GFAP immunoreactive astrocytes have retracted processes in the ZLC-methi and ZDF-methi groups compared to those observed in the ZLC or ZDF group. These phenomena are prominent in the ZDF-methi group compared to that in the ZLC-methi group. In contrast, the number of GFAP immunoreactive cells is not significantly different between groups. GCL: Granule cell layer; SP: stratum pyramidale. Scale bar: 100 μm.
The relative optical densities (ROD, I) and the relative number (J), expressed as a percentage of the value in the ZLC group of GFAP immunoreactivity in the dentate gyrus and hippocampal CA1 region per section of the ZLC, ZLC-methi, ZDF, and ZDF-methi groups. Differences between the means were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni's post-tests (10 sections per animal and 5 animals per group. aP < 0.05, vs. ZLC group; bP < 0.05, vs. ZDF group; cP < 0.05, vs. ZLC-methi group). The bars indicate mean ± standard error (SE).
