Figure 3.
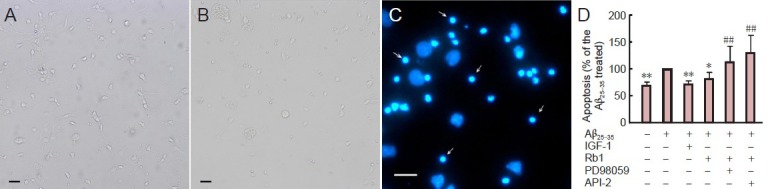
Ginsenoside Rb1 (Rb1) prevents apoptosis of hippocampal neurons and involves Akt and ERK1/2 signaling.
Primary hippocampal neurons were cultured for 24 hours and amyloid beta (25–35) (Aβ25–35) was added to the cultures for 30 minutes, then Rb1 with or without 10 μmol/L API-2 (Akt inhibitor) or 10 μmol/L PD98059 (MEK1/2 inhibitor) was added to the cultures for 48 hours. Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) was added as a positive control. Cells without Aβ25–35 treatment were considered normal controls. Hoechst-33258 staining was used to evaluate the apoptotic (condensed bright fluorescence, indicated by arrows) and viable (pallid blue fluorescence) nuclei. (A) Hippocampal neurons cultured for 3 days under inverted phase contrast microscope. (B) Hippocampal neurons cultured for 24 hours followed by exposure to Aβ25–35 for 48 hours under inverted phase contrast microscope. (C) Hoechst 33258 staining shows apoptotic (arrows) and viable cells. (A-C) Scale bars: 200 μm. (D) Percentage of apoptotic cells. Data expressed as mean ± SD (n = 9; one-way analysis of variance and Student-Newman-Keuls test). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. Aβ25–35; ##P < 0.01, vs. Rb1. Rb1 prevented apoptosis of hippocampal neurons after exposure to Aβ25–35. This effect was blocked by PD98059 and API-2.
