Figure 1.
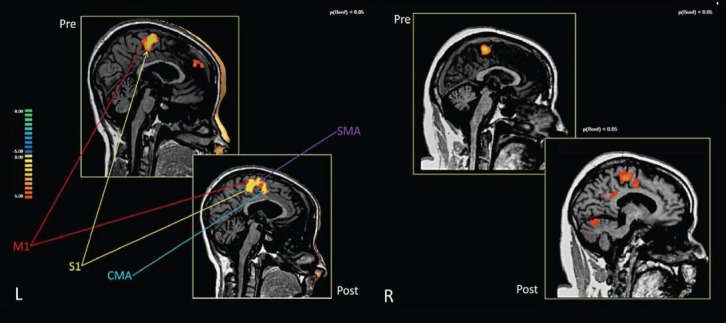
Brain activations in the pre- and post-training conditions of two chronic traumatic brain injury patients receiving a combined robotic and cognitive training for rehabilitation.
The highlighted warm areas designate signal intensity of brain activation. For the first patient at left side (L), combined training increased the recruitment of cingulate motor area and supplemental motor area in compensation of brain function. For the second case at right (R), combined training increased recruitment of more brain regions for compensation. M1: Primary motor cortex; S1: primary somatosensory cortex; CMA: cingulate motor area; SMA: supplemental motor area. Image courtesy Sacco et al. (2011) and Frontiers in Human Neurosciences.
