Figure 6.
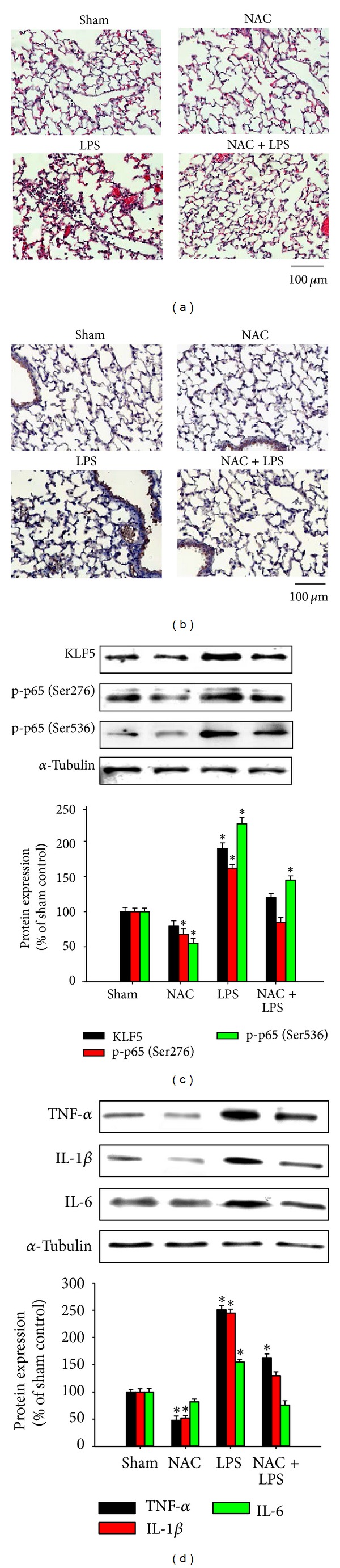
Krüppel-like factor 5, nuclear factor-kappaB subunit, and proinflammatory cytokine expression in lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) induced acute lung inflammation in mice. BALB/C mice were intraperitoneally injected with or without N-acetylcysteine (NAC; 150 mg/kg) for 1 h before intraperitoneal administration of LPS (20 mg/kg) for 8 h. Lung tissue sections were (a) stained with hematoxylin and eosin to observe the infiltration of cells and (b) analyzed immunohistochemically to evaluate KLF5 expression. A representative stained lung tissue from 3 independent experiments is shown. (c) KLF5, p65, phospho-p65 (Ser276), and phospho-p65 (Ser536) protein expression and (d) tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin- (IL-) 1β, and IL-6 expression were evaluated using western blotting. We observed histological changes including inflammatory cell infiltration, focal areas of fibrosis with collapsed air alveoli, and thickening of the alveolar wall (a) as well as upregulated KLF5 (b), p65, phospho-p65 (Ser276), and phospho-p65 (Ser536) protein expression (c) and upregulated TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 expression (d).
