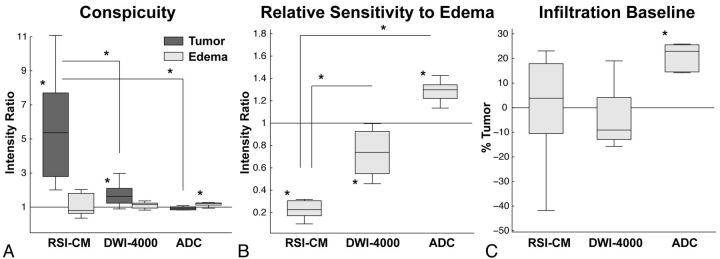
Fig 4.
Box-and-whisker plots of intensity ratios quantifying tumor and edema conspicuity (A) and relative sensitivity to edema (B). On each box, the central mark is the median, the edges of the box are the 25th and 75th percentiles, the whiskers represent data ranges, and the red dots indicate potential outliers. A, TC is significant on the RSI-CM (P = .001) and DWI-4000 (P = .005), but not on ADC (P = .11). TC is significantly greater on the RSI-CM compared with DWI-4000 (P = .002) and ADC (P < .001). B, RSE is significantly less in the RSI-CM versus DWI-4000 (P < .001) and ADC (P < .001). C, Box-and-whisker plots of the predicted infiltrative baseline, defined as the percentage of tumor signal required within edema to equalize the signal to normal-appearing WM. The predicted infiltrative baseline of ADC is significantly greater than that of the RSI-CM (P < .001) and DWI-4000 (P < .001). Note that negative data points may reflect tumor infiltrated edema.