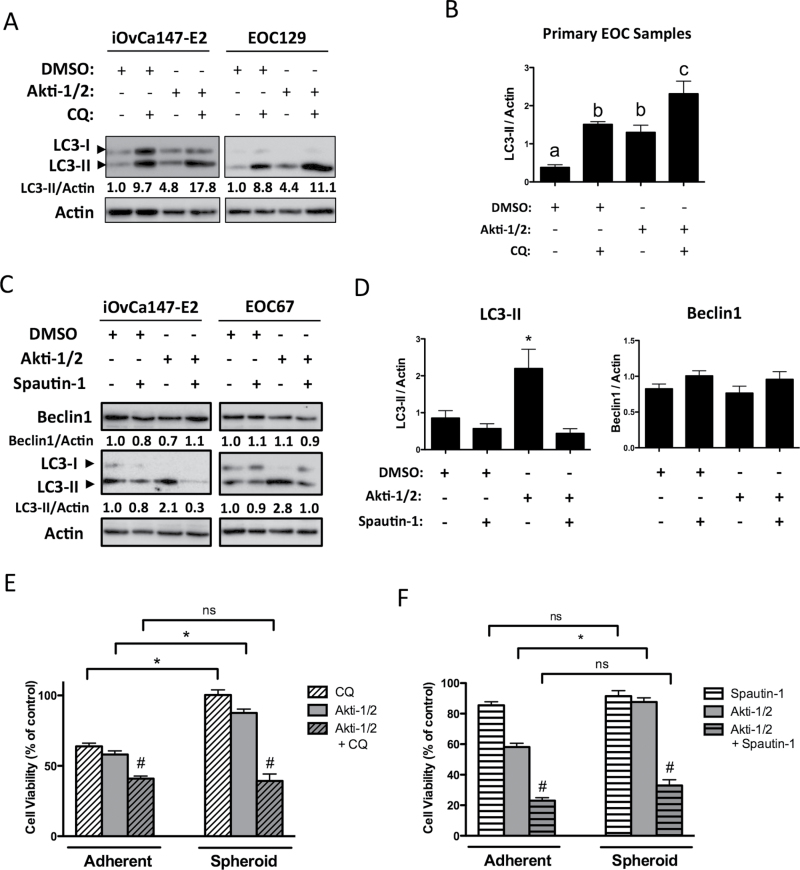
Fig. 6.
Spheroids are more sensitive to combined AKT and autophagy inhibition than either treatment alone. Non-adherent cells in 6-well ultra-low attachment plates were treated (Akti-1/2 5 μM, CQ 50 μM, Spautin-1 10 μM) at time of seeding and lysates obtained 24h post-treatment, and immunoblot was performed for indicated proteins. (A and C) Representative blots of iOvCa147-E2 and EOC129 cells (A) or iOvCa147-E2 and EOC67 cells are depicted. Quantification of Beclin-1 and LC3II expression relative to actin is shown, as determined using the Chemidoc System and ImageLab 4.1 software (Biorad). (B and D) Quantification of band intensity of LC3-II or Beclin-1 normalized to actin for multiple EOC samples (n = 4 or 5). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. One-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple comparison test compared means. Letters denote statistical significance (panel B, P ≤ 0.05; panel D, *P ≤ 0.01). (E and F) For viability assays, cells were seeded to parallel adherent or spheroid cultures, then treated following overnight incubation or at time of seeding, respectively. Viability was quantified by and normalized to DMSO vehicle control (set to 100%). Normalized viability data from individual EOC samples (n = 7) treated with (E) Akti-1/2 (EC50) ± CQ (25 μM) or (F) Akti-1/2 (EC50) ± Spautin-1 (10 μM) were pooled and one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple comparison test performed (*P ≤ 0.001). Drug combination more effectively decreased viability compared with single-agent treatments (# P ≤ 0.01). Data are represented as mean ± SEM.