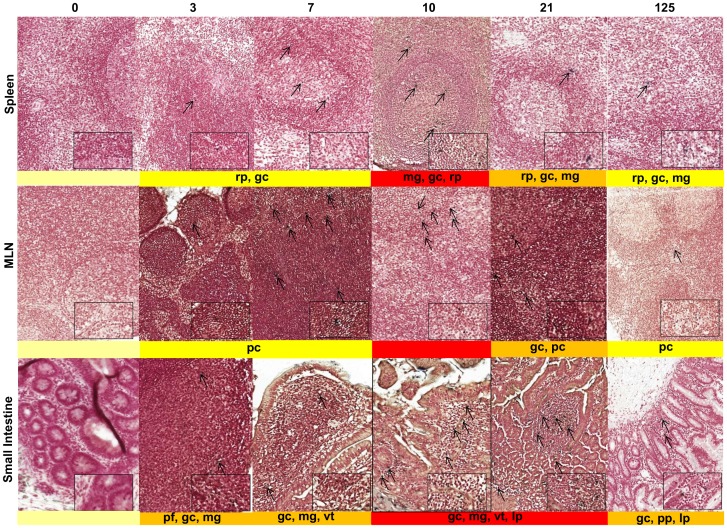
Figure 3. SIVmacC8 establishes persisting foci in infection in multiple lymphoid tissues.
Galleries of representative fields of in-situ hybridisation of sections of spleen, MLN and small intestine in MCM inoculated with SIVmacC8 and sacrificed at 0 (naïve) 3, 7, 10, 21 and 125 days post infection (d.p.i). Heatmap staining representing the overall frequency of foci of virus-infected cells in multiple fields is shown beneath individual panels. Location of foci of virus-infected cells are represented as indicated: pf – primary follicles, pp - peyers patches; pc – paracortex, rp – red pulp, gc – germinal centre, mg – follicular marginal/mantle zone, ms – medullary sinuses, lp – lamina propria, vt – villi tips within each main tissue type and indicated by arrows. Samples from naive, uninfected macaques are shown as controls. Magnification was ×20, main image; ×80 inset. In situ hybridisation for combined SIV gag/env/nef (g/e/n) messenger RNA conform to the same classification of staining intensity as IHC for comparative purposes: pale yellow (no staining, −); yellow (very low, +); dark yellow (medium, ++), red (high, +++), corresponding to the mean number of positive cells/mm2: + (0.5–6.8), ++ (6.9–13.8) and +++ (>13.8) cells/mm2 also represented in Table S1.