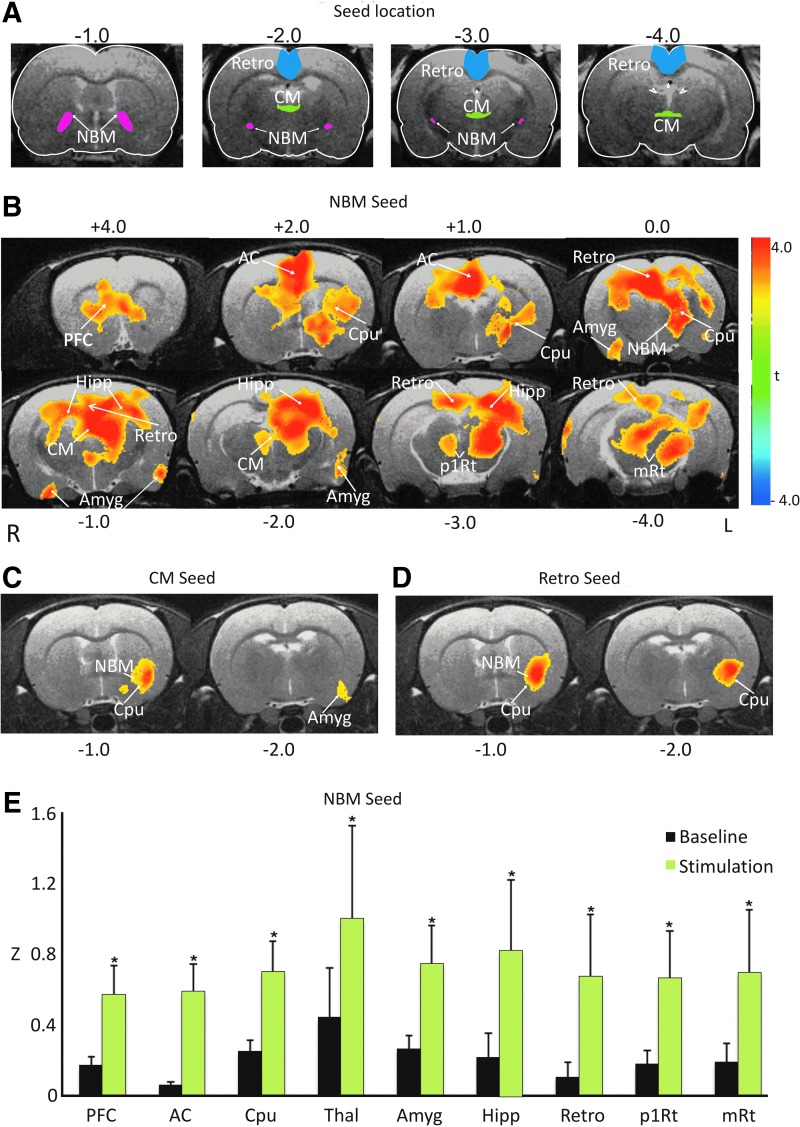
FIG. 3.
Effect of PnO stimulation on blood-oxygenation-level-dependent functional connectivity (FC). (A) Seed locations for the three that revealed significant regional changes after PnO stimulation. (B) Map of significant increases in FC using nucleus Basalis of Meynert (NBM) as seed from voxelwise t-test in all animals. Maps are overlaid on sample anatomical images. Color bar indicates t-range. Brain regions with significant FC increases (p<0.05) are caudate putamen (Cpu), prefrontal cortex (PFC), anterior cingulate (AC), hippocampus, retrosplenium (Retro), amygdala (Amyg), thalamus (Thal), and reticular formation (p1Rt and mRt). R: right, L: left. (C) Map of significant increases in FC using the central medial thalamic nucleus (CM) as seed. (D) The same using retrosplenium (Retro) as seed. (E) Regional averaged FC values of all animals during baseline (black bars) and after PnO stimulation (green bars), with seed voxels in the left NBM. *p<0.05 versus baseline. Error bars are±1 SD. All results are from group data after familywise multiple comparisons.