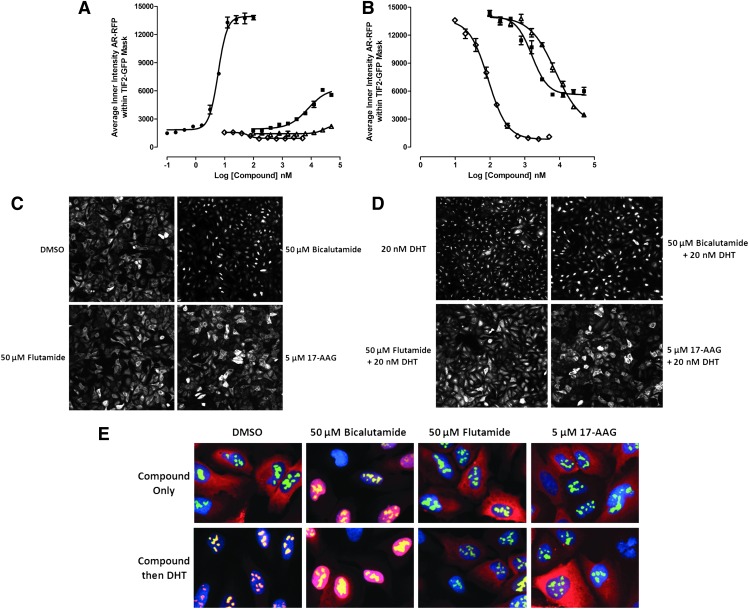
Fig. 6.
Antiandrogen and Hsp 90 inhibitor concentration responses in the AR-TIF2 PPIB assay. (A) DHT and inhibitor induced AR-TIF2 PPI responses. U-2 OS cells were coinfected with the AR-RFP and TIF2-GFP rAV biosensors, 2,500 cells were seeded into the wells of 384-well assay plates, cultured overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity, and then exposed to compounds at the indicated concentrations for 1 h. Cells were then fixed and stained with Hoechst, 20× images in three fluorescent channels were acquired on the IXU automated imaging platform, and the AR-TIF2 PPIs were quantified using the TE image analysis module as described previously. The mean±SD (n=3) average inner intensity of AR-RFP within the TIF2-GFP-positive nucleoli in cells exposed to the indicated concentrations of DHT (●), bicalutamide (■), flutamide (Δ), or 17-N-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG) (◊) are presented. Representative experimental data from one of the five independent experiments are shown. (B) Inhibition of DHT induced AR-TIF2 PPIs. U-2 OS cells were coinfected with the AR-RFP and TIF2-GFP rAV biosensors, 2,500 cells were seeded into the wells of 384-well assay plates, cultured overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity, and then exposed to compounds at the indicated concentrations for 1 h. Cells were then treated with 20 nM DHT for 30 min, fixed and stained with Hoechst, 20× images in three fluorescent channels were acquired on the IXU automated imaging platform, and the AR-TIF2 PPIs were quantified using the TE image analysis module as described previously. The mean±SD (n=3) average inner intensity of AR-RFP within the TIF2-GFP-positive nucleoli in cells exposed to the indicated concentrations of bicalutamide (■), flutamide (Δ), or 17-AAG (◊) for 1 h and then treated with 20 nM DHT are presented. Representative experimental data from one of the five independent experiments are shown. (C) Images of the AR-RFP phenotype in cells preexposed to compounds for 1 h. U-2 OS cells were coinfected with the AR-RFP and TIF2-GFP rAV biosensors, 2,500 cells were seeded into the wells of 384-well assay plates, cultured overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity, and then exposed to compounds at a variety of concentrations for 1 h. Cells were then fixed and stained with Hoechst, and 20× images in three fluorescent channels were acquired on the IXU automated imaging platform. Grayscale images of the AR-RFP distribution phenotype of coinfected U-2 OS cells exposed to 0.5% DMSO, 50 μM bicalutamide in 0.5% DMSO, 50 μM flutamide in 0.5% DMSO, or 5 μM 17-AAG in 0.5% DMSO for 1 h. Representative images from one of the five independent experiments are shown. (D) Images of AR-RFP phenotype in cells preexposed to compounds for 1 h and then treated with 20 nM DHT for 30 min. U-2 OS cells were coinfected with the AR-RFP and TIF2-GFP rAV biosensors, 2,500 cells were seeded into the wells of 384-well assay plates, cultured overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity, and then exposed to compounds at a variety of concentrations for 1 h. Cells were then treated with 20 nM DHT for 30 min, fixed and stained with Hoechst, and 20× images in three fluorescent channels were acquired on the IXU automated imaging platform. Grayscale images of the AR-RFP distribution phenotype of coinfected U-2 OS cells preexposed to 0.5% DMSO, 50 μM bicalutamide in 0.5% DMSO, 50 μM flutamide in 0.5% DMSO, or 5 μM 17-AAG in 0.5% DMSO for 1 h before treatment with 20 nM DHT. Representative images from one of the five independent experiments are shown. (E) 40× color composite images of compound induced AR-TIF2 biosensor phenotypes±20 nM DHT. 40× color composite images of the AR-TIF2 biosensor phenotypes of coinfected U-2 OS cells preexposed to 0.5% DMSO, 50 μM bicalutamide in 0.5% DMSO, 50 μM flutamide in 0.5% DMSO, or 5 μM 17-AAG in 0.5% DMSO for 1 h before 30 treatment±20 nM DHT. Representative images from one of the two independent experiments are shown. Ch1 Hoechst, blue; Ch2 TIF2-GFP, green; Ch3 AR-RFP, red; AR-TIF2 PPIs, yellow.