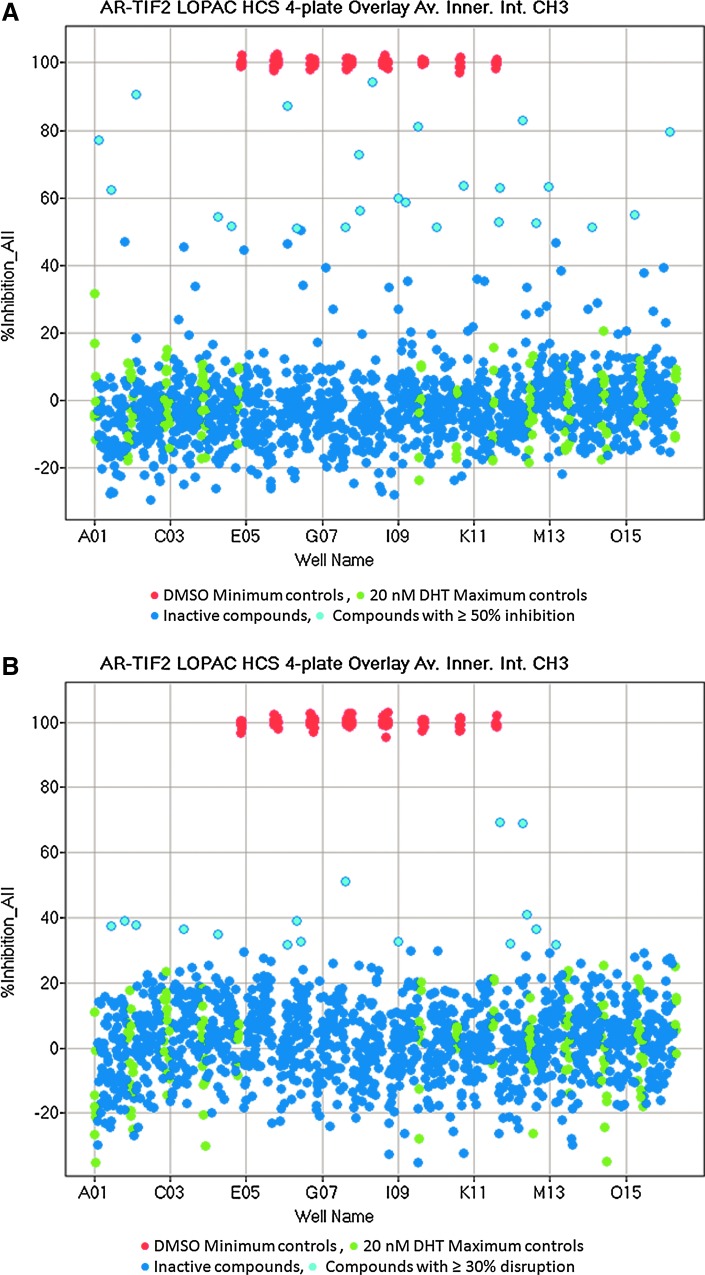
Fig. 7.
Library of Pharmacologically Active Compounds (LOPAC) screen to identify compounds that block DHT-induced AR-TIF2 PPI formation or that disrupt preexisting AR-TIF2 complexes. (A) Overlay scatter plot of the percent inhibition of DHT-induced AR-TIF2 PPI formation from the 4×384-well assay plates of the 1,280 compound LOPAC set. U-2 OS cells were coinfected with the AR-RFP and TIF2-GFP rAV biosensors, 2,500 cells were seeded into the wells of 4×384-well assay plates, cultured overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity, and then exposed to the LOPAC compounds at 20 μM (0.2% DMSO) for 1 h. Cells were then treated with 20 nM DHT for 30 min, fixed and stained with Hoechst, 20× images in three fluorescent channels were acquired on the IXU automated imaging platform, and the AR-TIF2 PPIs were quantified using the TE image analysis module as described previously. The mean average inner intensity values of AR-RFP within the TIF2-GFP-positive nucleoli of the 0.2% DMSO minimum (Min) plate control wells (n=32) and the 20 nM DHT maximum (Max) plate control wells (n=32) were used to normalize the mean average inner intensity values of AR-RFP within the TIF2-GFP-positive nucleoli of compound-treated wells and to represent 100% and 0% inhibition of DHT-induced AR-TIF2 PPI formation, respectively. Max (green) controls, Min (red) controls, inactive (<50% inhibition) compound-treated wells (dark blue), and active (≥50% inhibition) compound-treated wells (light blue). Representative experimental data from one of the two independent LOPAC screens are presented. (B) Overlay scatter plot of the percent disruption of preexisting AR-TIF2 PPI complexes from the 4×384-well assay plates of the 1,280 compound LOPAC set. U-2 OS cells were coinfected with the AR-RFP and TIF2-GFP rAV biosensors, 2,500 cells were seeded into the wells of 4×384-well assay plates, cultured overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity, and then treated with 20 nM DHT for 30 min to induce AR-TIF2 PPI formation. Cells were then exposed to the LOPAC compounds at 20 μM (0.2% DMSO) for 1 h, fixed and stained with Hoechst, 20× images in three fluorescent channels were acquired on the IXU automated imaging platform, and the AR-TIF2 PPIs were quantified using the TE image analysis module as described previously. The mean average inner intensity values of AR-RFP within the TIF2-GFP-positive nucleoli of the 0.2% DMSO Min plate control wells (n=32) and the 20 nM DHT Max plate control wells (n=32) were used to normalize the mean average inner intensity values of AR-RFP within the TIF2-GFP-positive nucleoli of compound-treated wells and to represent 100% and 0% disruption of preexisting AR-TIF2 PPI complexes, respectively. Max (green) controls, Min (red) controls, inactive (<30% inhibition) compound-treated wells (dark blue), and active (≥30% inhibition) compound-treated wells (light blue). Representative experimental data from one of the two independent LOPAC screens are presented.