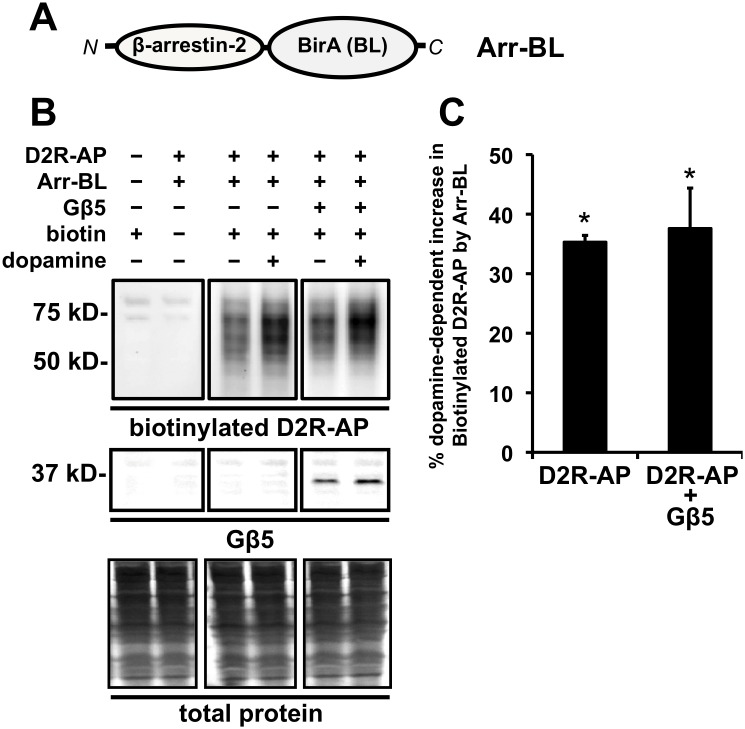
Figure 7. Effect of Gβ5 coexpression on arrestin recruitment to D2R-AP upon dopamine treatment as assessed by an in-cell “proximity biotin transfer assay”.
A. Schematic of the Arr-BL construct, a fusion of arrestin and BirA, an E. coli derived biotin ligase (BL) enzyme that specifically biotinylates a unique acceptor peptide (AP) sequence. N and C refer to the N- and C-terminus, respectively, of the fusion protein. B. Representative images from a Western blot depicting total cellular biotinylated D2R-AP by coexpressed Arr-BL (top panels) and coexpressed Gβ5 (bottom panels). The top left panel represents samples prepared from cells that were untransfected with either D2R-AP (−) or Arr-BL (−) and treated with 10 µM biotin for 2 min (biotin +, left) or samples that were transfected with both D2R-AP (+) and Arr-BL (+) and not treated with biotin (biotin −, right). The top center panel represents samples prepared from cells which were transfected with both D2R-AP (+) and Arr-BL (+) and treated with vehicle (dopamine −, left) or 10 µM dopamine for 30 min (dopamine +, right) and treated with biotin. The top right panel represents samples prepared from cells which were transfected with both D2R-AP (+), Arr-BL (+), and Gβ5 (+) and treated with vehicle (dopamine −, left) or 10 µM dopamine for 30 minutes (dopamine +, right) and treated with biotin (+).D2R-AP biotinylated by Arr-BL was detected by probing the blots with streptavidin. The middle panels represent corresponding western blots from samples in the upper panel probed for Gβ5. The bottom panels represent corresponding western blots from samples in the upper panel stained for total protein. C. Quantification of the relative levels of D2R-AP biotinylated by Arr-BL in response to dopamine treatment (10 µM for 30 min) in cells expressing only D2R-AP and Arr-BL or cells expressing D2R-AP, Arr-BL, and Gβ5. The biotinylated D2R-AP signal is expressed as a percentage of biotinylated D2R-AP signal from cells that were not treated with dopamine (mean ± SEM; n = 4, *p<0.05, t-test, compared to biotinyalted D2R-AP signal from corresponding cells not treated with dopamine).