Table 2. Parameters involved in the swine breeding farm model, with definitions, values and the sources of the values.
| Model parameter | Meaning | Value | Experimental source of value |
| DISEASE PARAMETERS | |||
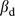
|
Direct transmission rate for sows and gilts | 0.285 day−1 * (95% confidence interval: 0.091–0.9) | Experimental data from Romagosa et al. [14] (mean of transmission values from non-vaccinated treatment group) |
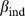
|
Indirect transmission rate for sows and gilts | 0.0016 day−1 * 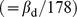
|
Calculated from experimental data from Allerson et al. [10] |
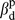
|
Direct transmission rate for piglets | 0.218 day−1 * (95% confidence interval: 0.147–0.310) | Experimental data from Allerson et al. [13] (transmission rate for non-vaccinated treatment group) |
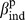
|
Indirect transmission rate for piglets | 0.001 day−1 * | Extrapolation from experimental data from Allerson et al. [10]; we assume 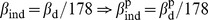
|
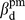
|
Direct transmission rate for piglets with maternal immunity | 0.014 day−1 * (95% confidence interval: 0.001–0.061) | Experimental data from Allerson et al. [13] |
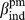
|
Indirect transmission rate for piglets with maternal immunity | 0.00008 day−1 * | Extrapolation from experimental data from Allerson et al. [10] |

|
Reciprocal of average duration of latent/exposed period | 1/2 day−1 | Survey of swine influenza literature [24] |

|
Reciprocal of average duration of infectious period (or recovery rate) | 1/5 day−1 | Survey of swine influenza literature [3], [14], [24], [26] |
| VACCINATION PARAMETERS | |||
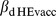
|
Direct transmission rate for pigs vaccinated with heterologous vaccine | 0.0275 day−1 ** (95% confidence interval: 0.001–0.115) | Experimental data from Romagosa et al. [14] (mean of transmission values from heterologously vaccinated treatment group) |
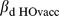
|
Direct transmission rate for pigs vaccinated with homologous vaccine | 0 day−1 ** (95% confidence interval: 0–0.052) | Experimental data from Romagosa et al. [14] (no transmission occurred to pigs in homologously vaccinated treatment group) |
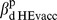
|
Direct transmission rate for piglets when mother vaccinated with heterologous vaccine | 0.174 day−1 ** (95% confidence interval: 0.118–0.246) | Experimental data from Allerson et al. [13] (transmission rate from heterologously vaccinated treatment group) |

|
Direct transmission rate for piglets when mother vaccinated with homologous vaccine | 0.014 day−1 ** (95% confidence interval: 0.001–0.061) | Experimental data from Allerson et al. [13] (transmission rate for homologously vaccinated treatment group) |
| Indirect transmission rates for each vaccine type are extrapolated from experimental data from Allerson et al. [10]. | |||
| SWINE FARM PRODUCTION PARAMETERS | |||
| b | Birth rate | 12 live births per litter per sow (between days 2 and 7 each week) | From expert knowledge of swine farm and PigCHAMP website (www.pigchamp.com/LinkClick.aspx?fileticket = NMdM5F73gKE%3d&tabid = 115) |
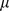
|
Natural death rate for sows and gilts (i.e. death rate not including culled animals) | 0.0004 day−1 | When combined with the cull, this value gives a total death rate of 50% per year (from expert knowledge of swine farm and PigCHAMP website) |
|
Natural death rate for piglets | 0.005 day−1 | Corresponds to a death rate of 10% from birth to weaning (from expert knowledge of swine farm and PigCHAMP website) |
The point/exact transmission values are used for the main simulations presented in this paper. “*” indicate transmission values that are varied across the range of their 95% confidence intervals for the model with variability in transmission. “**” similarly indicate the vaccination parameters that are varied for a sensitivity analysis.
