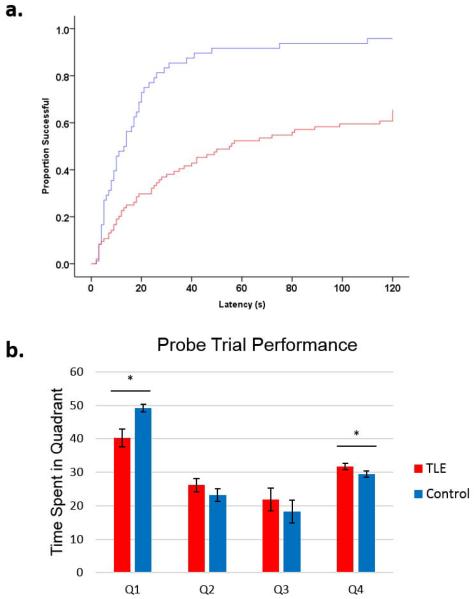
Figure 1.
TLE rats show marked deficits in spatial learning in the Morris Water Maze task. Rats were trained to find the platform in the water maze task 4 times each day for 4 consecutive days followed by a probe trial on the final day. (a) Latency to platform time-to-event curves showing the effect of TLE. The y-axis is the proportion of animals that have reached the platform and the x-axis is latency to platform in seconds. For example, when trials are modeled in, at 60 seconds, ~90% of controls had found the platform while only ~50% of TLE rats had found the platform. When days and trials were modeled using Cox regression model, TLE rats were 0.31±0.11 as likely to find the platform compared to controls.(b) In the probe trial, TLE rats spent less time in the platform quadrant (Q1, p=0.044) and more time in the opposing quadrant (Q4, p=0.001). TLE rats showed several impairments in spatial learning and memory, as was previously shown in this model.