Figure 6.
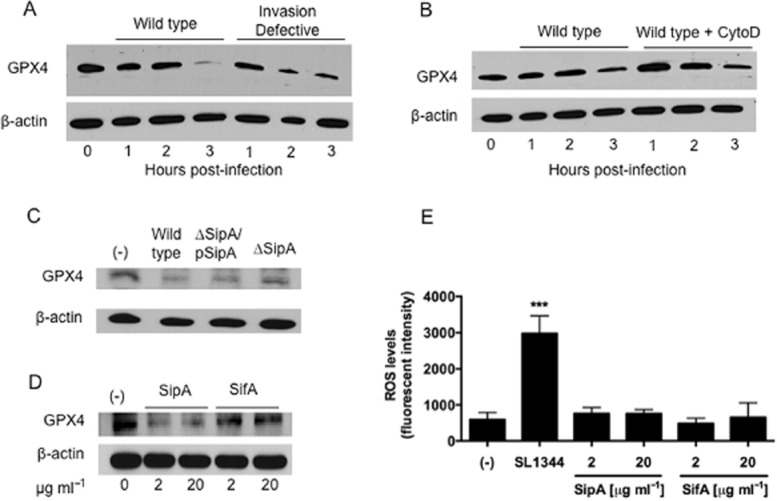
S. Typhimurium-induced decreased GPX4 expression is through the secreted effector SipA and does not require bacterial entry.
A. HCT-8 intestinal epithelial cells were infected apically with wild-type S. Typhimurium SL1344 or the isogenic invasion-defective strain VV341 for the indicated time points. Whole cell lysates were then extracted and the proteins normalized and Western blotted for GPX4.
B. HCT-8 cells were treated with 5 μg ml−1 of cytochalasin D or HBSS+ (negative control) for 45 min, infected with wild-type SL1344 for the indicated time points, and then analysed for GPX4 expression as above.
C. HCT-8 cells were infected with wild-type SL1344, the isogenic SipA-deficient strain EE633 (ΔSipA) or the SipA-complemented strain AJK63 (ΔSipA/pSipA) for 1 h, and then analysed for GPX4 expression.
D. HCT-8 cells were exposed on their apical surface to exogenous S. Typhimurium effectors SipA-HA or GST-SifA for 1 h, and then analysed for GPX4 expression.
E. SipA does not induce an increase in overall levels of ROS. The levels of ROS production in untreated cells and cells exposed to SipA or SifA for 90 min were not significantly different (The symbol ‘***’ indicates statistical significance, using the Student's t-test; P < 0.01).
