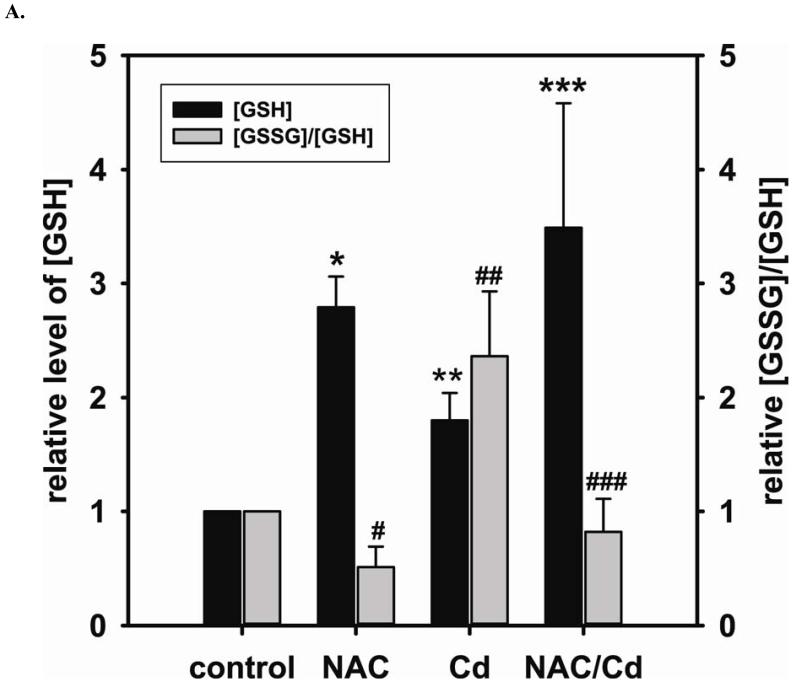
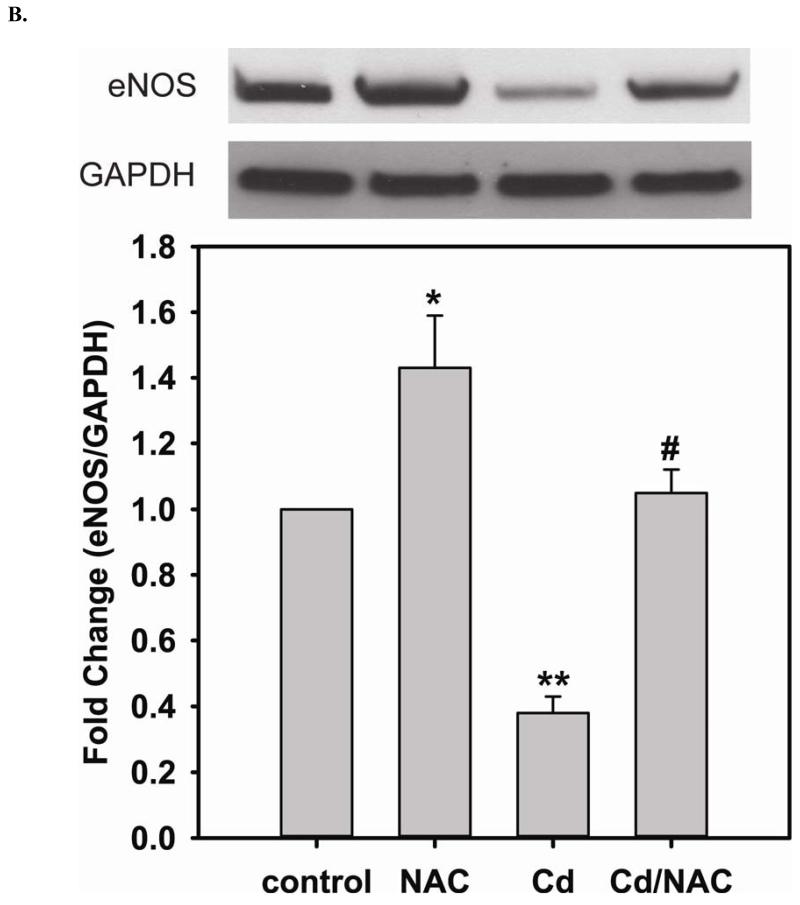
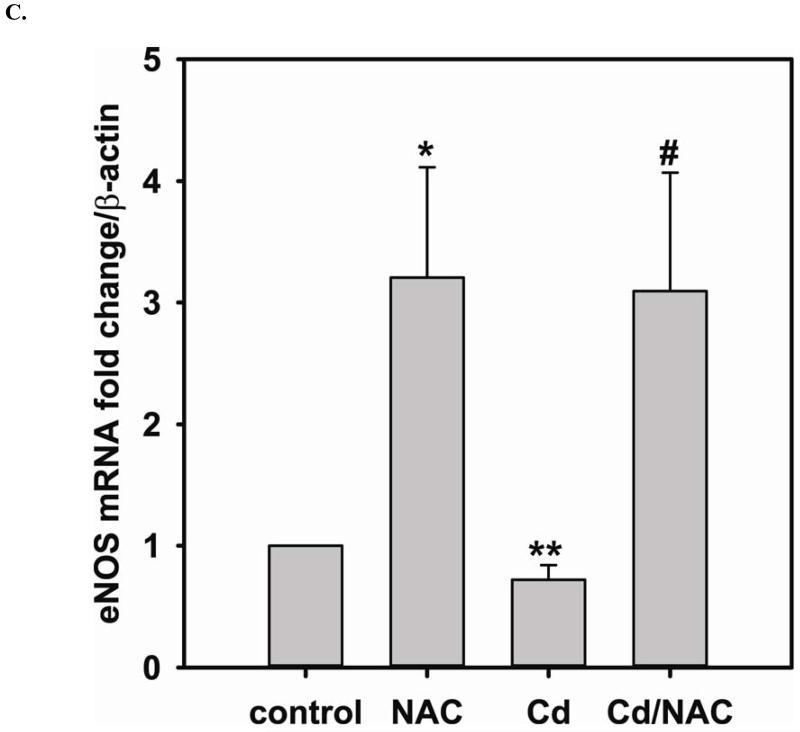
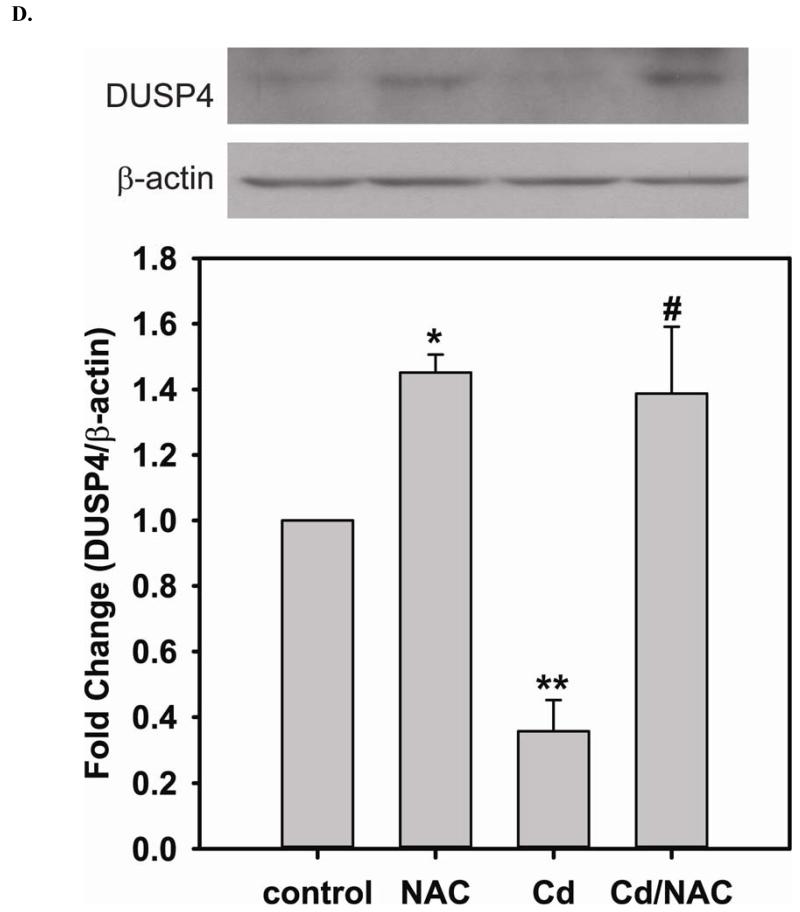
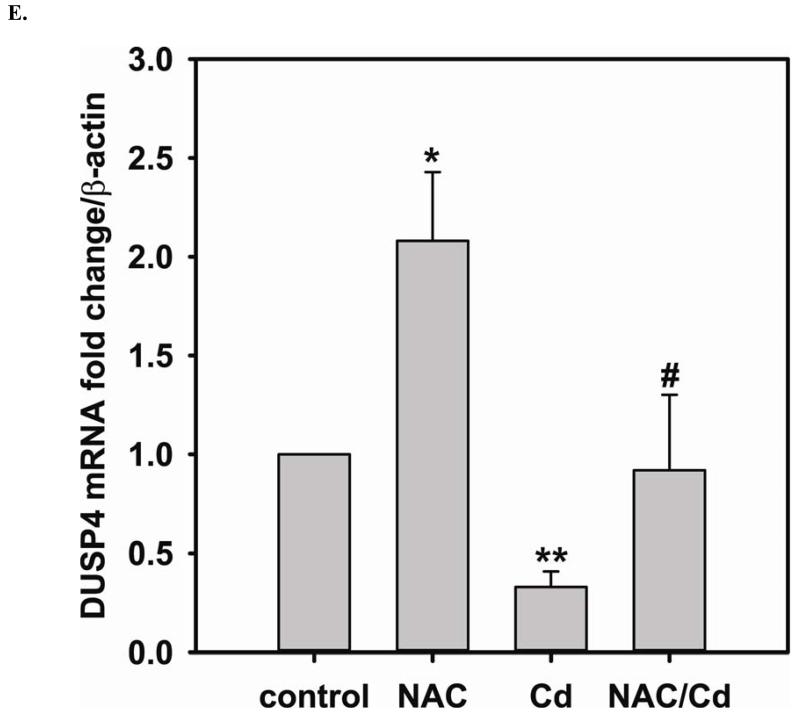
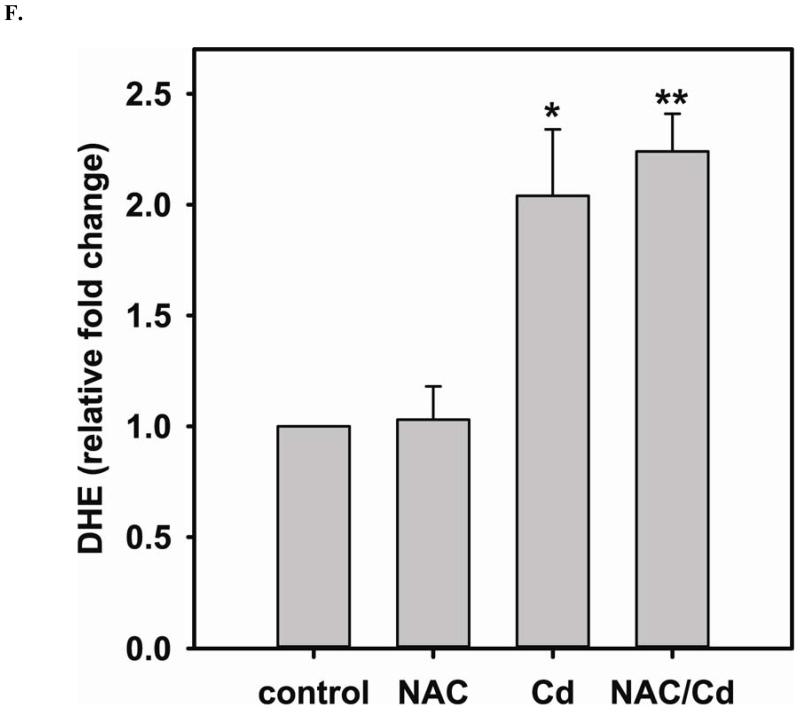
FIGURE 3. Long-term exposure to Cd2+ leads to the degradation of eNOS and DUSP4 while NAC treatment promotes their transcription and prevents protein degradation, providing a protective effect in BAECs.
A. NAC treatment protects endothelial cells from Cd2+-induced oxidative stress via the increase intracellular GSH and the decrease in [GSSG]/[GSH] ratio. The intracellular GSH and the ratio of [GSSG]/[GSH] are determined by HPLC. Long-term Cd2+ exposure dramatically increased intracellular [GSSG]/[GSH] ratio. NAC treatment reversed this oxidative stress. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3; P < 0.05 versus control. B. Upper panel is the immunoblotting against eNOS. Lower panel is the immunoblotting for GAPDH, the loading control. Densitometric analysis of the immunoblots reveals that long-term exposure to 100 μM Cd2+ leads to eNOS degradation (0.38 ± 0.05 fold change versus control; ** P < 0.001). NAC treatment prevents this Cd2+-induced eNOS degradation. C. NAC increases eNOS transcription. Overnight treatment with NAC leads to a significant increase in eNOS transcription (3.21 ± 0.91 fold increase versus control; * P < 0.05), and NAC co-treatment with Cd2+ (3.09 ± 0.98 fold versus control; # P < 0.05) was able to rescue the Cd2+-induced degradation in eNOS mRNA (0.72 ± 0.12 fold of control; ** P < 0.01). D. Upper panel is the immunoblotting against DUSP4. Lower panel is the immunoblotting for β-actin, the loading control. Long-term exposure to 100 μM Cd2+ leads to DUSP4 degradation (0.36 ± 0.09 fold change versus control; ** P < 0.05). NAC treatment reverses this Cd2+-induced degradation. All experiments were performed at least in triplicate. E. NAC treatment promotes DUSP4 transcription in endothelial cells. The effect of NAC/Cd2+ treatment on DUSP4 transcription closely mirrored that seen in the protein blotting. NAC doubled DUSP4 mRNA (2.08 ± 0.35 fold versus control; * P < 0.01) whereas Cd2+ less than halved it (0.33 ± 0.08 fold; ** P < 0.001). However, unlike the protein effect, co-treatment with NAC and Cd2+ only returned DUSP4 mRNA to control level. F. Measurement of superoxide from endothelial cells. Cd2+ exposure induced cellular superoxide generation (2.04 ± 0.30 fold versus control; * P < 0.05); however, NAC treatment did not diminish Cd2+-induced superoxide generation (2.24 ± 0.17 fold versus control; ** P< 0.005).