Figure 4.
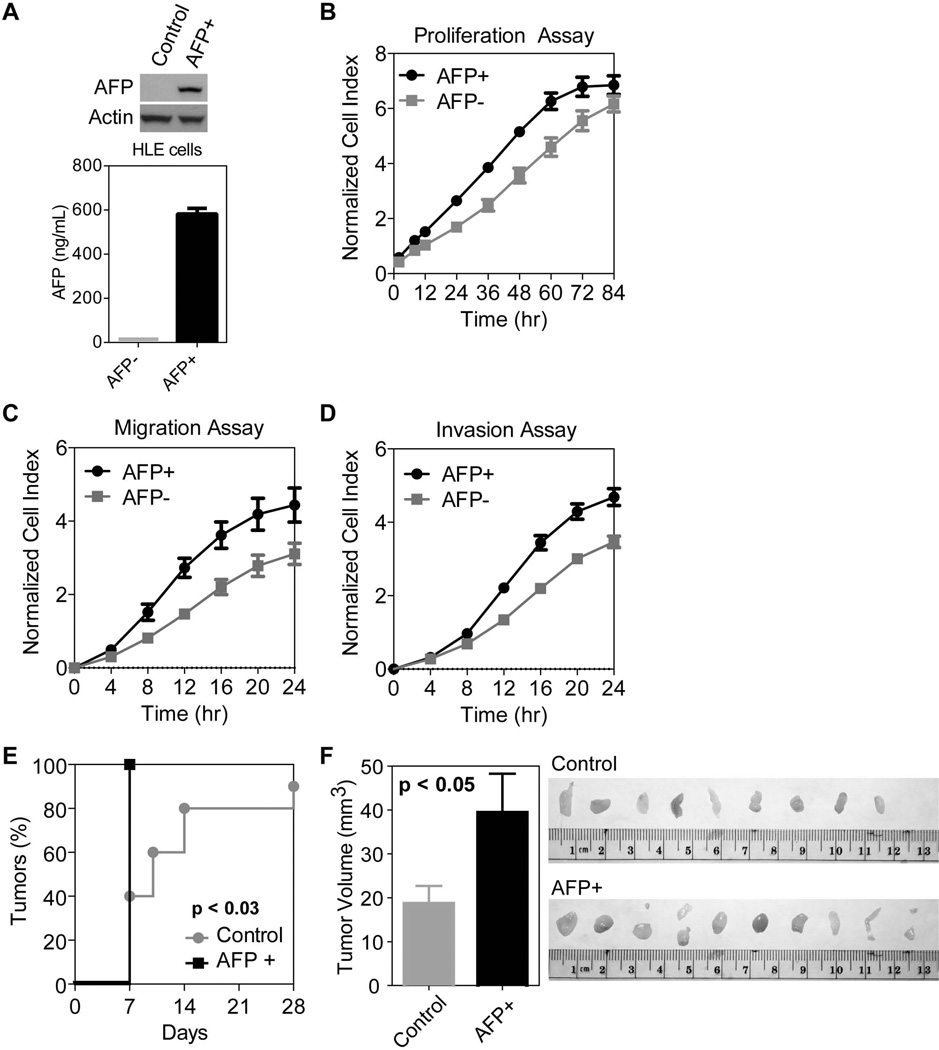
AFP expression promotes cell growth, cell migration and invasion in vitro and tumorigenesis in vivo. A) AFP expression detected by western (top) and ELISA (bottom) in stable AFP+ versus control HLE cells. AFP is only expressed and secreted in cells infected with a lentivirus incorporating the AFP gene. B) Stable AFP+ cells show more rapid proliferation compared to control cells. The growth rate of AFP+ cells is significantly faster on days 1–3 (p<0.01). There are three replicates per time point and error bars represent standard deviation. C) AFP expression induces increased migratory capacity, significantly different from control cells starting at 8 hours (p<0.01). There are three replicates per times point and error bars represent standard deviation. D) AFP expression also leads to increased invasion significantly different from control cells starting at 12 hours (p<0.01). There are three replicates per time point and error bars represent standard deviation. E) Tumor incidence is significantly faster in nude mice injected with 0.5×106 AFP+ cells AFP+ cells compared to 0.5×106 AFP− control HLE cells (p<0.05). After 1 week, all mice in the AFP+ group carried a tumor compared to less than half of the control group. F) Quantification of tumor volume (mm3) shows a significant difference between the size of control versus AFP+ tumors (p<0.05). Error bars represent mean plus standard error. Image of tumors extracted from the control and AFP+ groups after 4 weeks.