Fig. 3.
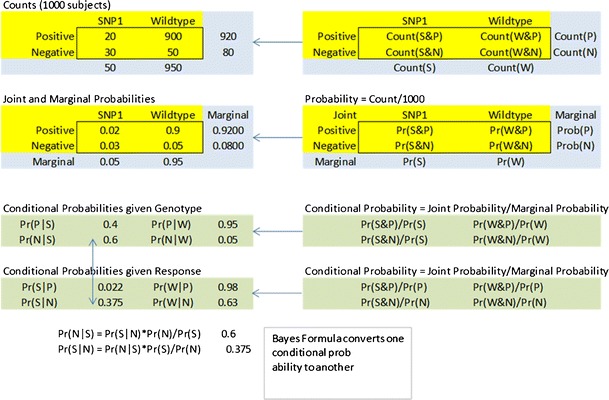
Conditional probabilities and Bayes theorem. One thousand patients were tested for the presence of a particular SNP (possible values are SNP1 present (S) or wild-type (W)) and were also tested for response to a drug (possible values are positive response (P) or negative response (N)). A two-way table of the counts for each of the four possible outcomes is converted to the joint and marginal probabilities (Pr) by dividing by the total number of subjects. There are two types of conditional probabilities—the conditional probability of a drug response given the genotype is known, and the conditional probability of the genotype given the drug response is known. Bayes formula allows the conversion between the two types of conditional probability
