Fig. 4.
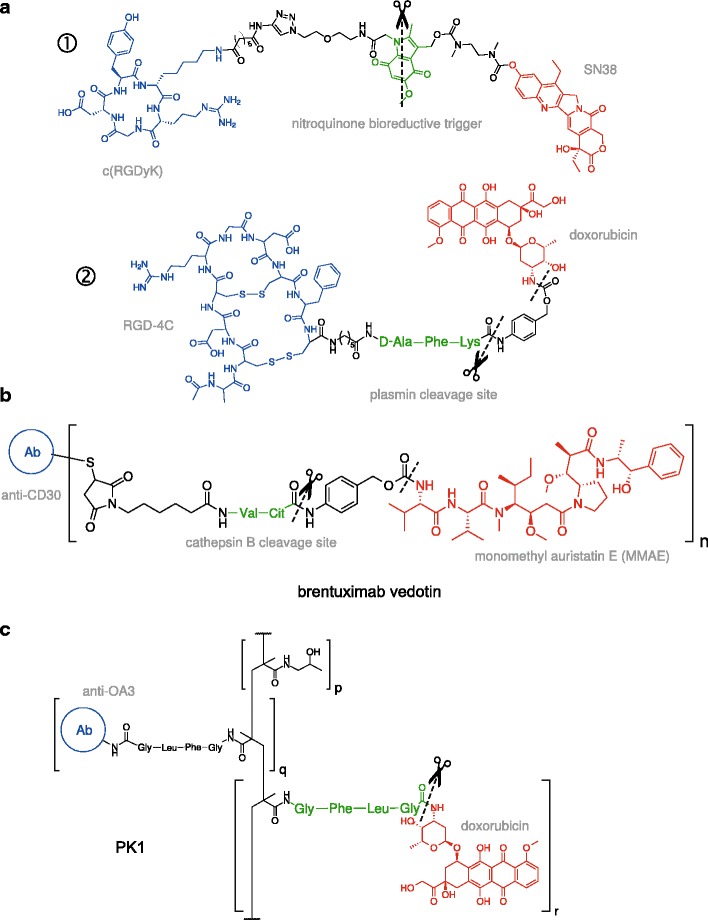
Conditionally bispecific prodrug conjugates. Shown are illustrative examples of cytotoxic agents (red) that are covalently linked to a promoiety that targets two independent markers in a sequential, conditional manner. Receptor-targeting ligands are colored in blue and substrates for target-specific cleavage in green. a “Low-MW” prodrug conjugates targeting cell-surface integrins with cyclic RGD motifs. ① A prodrug conjugate of SN38 (the active form of irinotecan) linked by a nitroquinone trigger. Specific two-electron reduction of the indole nitrogen by intracellular DT-diaphorase (DTD) leads to fragmentation of the linker and drug release (96). ② A doxorubicin conjugate linked by a substrate for plasmin (97). Plasmin cleavage conditionally triggers 1,6-elimination of the adjacent p-aminobenzyl alcohol (PABOH), releasing the free drug. b Brentuximab vedotin is a conjugate of monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), an anti-mitotic agent, with the anti-CD30 antibody brentuximab (98). Upon endocytosis, cleavage of the valine-citrulline linker by lysosomal cathepsin B, followed by decomposition of the adjacent PABOH moiety, releases MMAE (99). This ADC (Adcetris®) is currently approved for use or in clinical trials for several lymphomas. c A targeted HPMA-doxorubicin (termed PK1) in which DOX and an antibody targeting the surface antigen OA3 on ovarian cancer cells are attached to polymeric HPMA via a peptide substrate (GFLG) for lysosomal cathepsin B (100)
