Fig. 5.
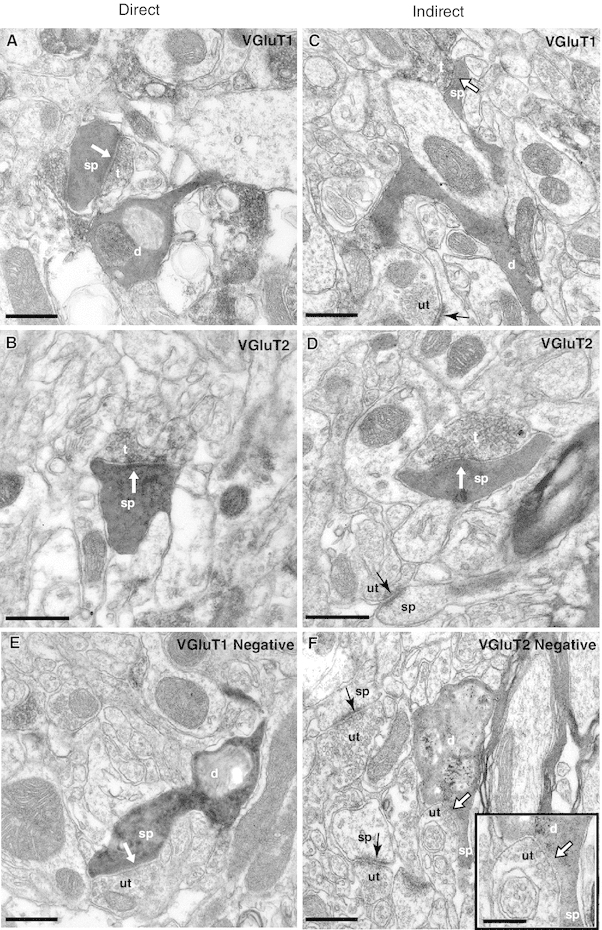
Individual direct and indirect pathway MSNs receive convergent VGluT1-positive (cortical) and VGluT2-positive (thalamic) synaptic input. Dendrites (d) and spines (sp) of an individually labelled direct pathway MSN (a, b, e) and an individually labelled indirect pathway (c, d, f). MSNs were identified by the dense black reaction product in the cytoplasm. a, b Spines (sp) of the direct pathway MSNs receive synaptic input (white arrows) from both VGluT1-positive (a) and VGluT2-positive (b) terminals (t). (e) A spine of the same neuron receives input (white arrow) from a VGluT1-negative terminal (ut) which is likely to be of thalamic origin. c, d Spines (sp) of the indirect pathway MSN also receive synaptic input (white arrows) from both VGluT1-positive (c) and VGluT2-positive (d) terminals (t). (f) A spine of the same neuron receives input (white arrow) from a VGluT2-negative terminal (ut) which is likely to be of cortical origin. Note also the unlabelled terminals (ut) forming synapses (black arrows) with unlabelled spines in (B) and (F). Scale bars 200 nm, inset in F 100 nm
