Figure 1. Expression and subcellular localization of Nek1 in renal cell carcinoma cell lines.
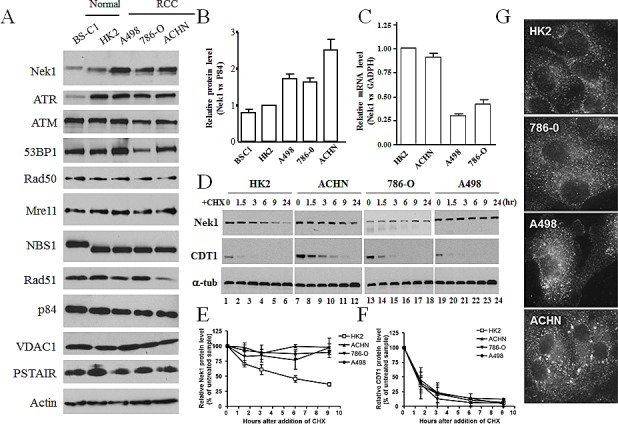
A & B. Nek1 expression in renal cell carcinoma cell lines. Total cell lysates were prepared from a normal monkey diploid kidney cells (BS-C1), normal human renal diploid cells (HK2), and three human renal cell carcinoma cell lines (A498, 786-O, and ACHN). Protein expression was analyzed by Western blotting using several antibodies. To control for total protein loading, p84, PSTAIR, VDAC1, and actin, were analyzed from the same samples. Nek1 expression in HK2 cells was normalized and given a value of 1. The relative amounts of Nek1 expressed in BS-C1, A498, 786-O, and ACHN cells were then expressed as fold-difference relative to HK2. Results represent analysis and quantification of three independent blots (means s.e.m.). C. Expression of Nek1 mRNA in RCC cells. Total RNA was purified from RCC cells. After reverse transcription, the resulting cDNAs were analyzed for Nek1 and GADPH expression using real-time PCR. Nek1 expression was normalized to GADPH, and expression in HK2 cells was again given a value of 1. D-F. Nek1 protein is stable in RCC cells. D. RCC and HK2 cells were treated with 100ug/ml cycloheximide for indicated time and level of Nek1 protein was detected by anti-Nek1 antibodies. Level of CDT1 was determined as control for the effect of cycloheximide. Nek1 (E) and CDT1 (F) protein levels were normalized with tubulin and expression as 100% at time zero. The protein amount was then plot against time as a mean from three independent experiments. Nek1 protein was stable in RCC cells. G. Subcellular localization of Nek1 in renal cell carcinoma. Cells in the exponential growth phase were grown on coverslipes, fixed with 4% neutral buffered formalin and then incubated with rabbit polyclonal anti-Nek1 primary antibodies and fluorescence-tagged anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibodies. Nek1 is localized primarily in the cytoplasm of all cells.
