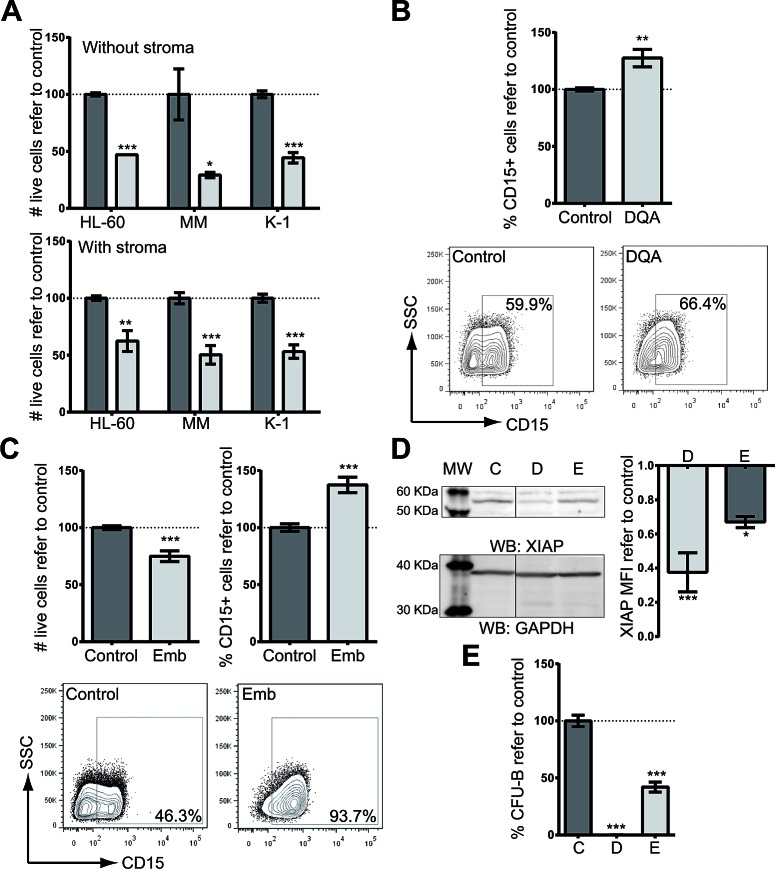
Figure 1. XIAP inhibitor treatment induces cytotoxicity and differentiation on AML cell lines.
A. Cytotoxicity in HL-60, MonoMac-1 (MM) and Kasumi-1 (K-1) AML cell lines resulting from treatment with 5 μM DQA for 48 h in the absence (upper panel) or presence of HS-5 stroma cells (lower panel). Y-axis: relative number of live cells as assessed by flow cytometry (7-AAD−). B. Up-regulation of CD15 surface expression, measured by flow cytometry in AML cell lines (HL-60, KG-1, MonoMac-1 and Kasumi-1) treated with 5 μM DQA. Data from all AML cell lines are presented combined. Frequency of CD15-positive population normalized against control-treated samples is represented. CD15 surface expression representative plot of HL-60 untreated (left) or treated with 5 μM DQA (right). C. HL-60, Kasumi-1, MonoMac-1 and KG-1 AML cells were treated with different concentrations of Embelin for 48 h. Cell viability (upper left panel) and CD15 surface expression (upper right panel) were measured by flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry plot of HL-60 untreated (left) or treated with 10 μM Embelin (right). D. XIAP protein was detected by Western blot upon DQA (D) and Emb (E) treatment of HL-60 cells. GAPDH was used as loading control. MFI refer to GAPDH and vehicle-treated control is represented. E. HL-60 cells were treated for 18 h with 5 μM DQA (left) and 10 μM embelin (right). Colonies were counted at day 7. * p<0.05; ** p<0.005; *** p<0.0005. Error bars correspond to SEM.