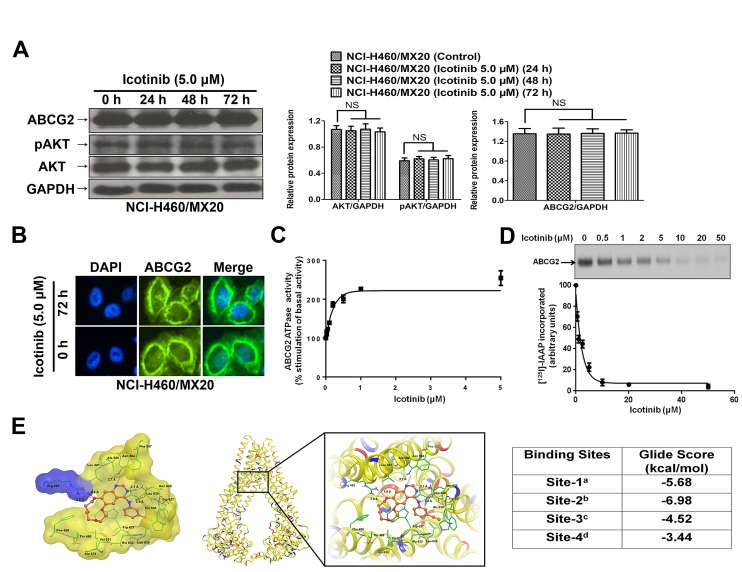
Fig. 3. The effect of Icotinib on the expression levels of pAKT, total AKT, ABCG2, the subcellular localization of ABCG2, ATPase activity, the photoaffinity labeling with [125I]-IAAP, and its docking in the homology model of ABCG2.
A. Effect of Icotinib at 5.0 μM on the expression level of pAKT, total AKT, and ABCG2 in NCI-H460/MX20 cell line. The protein levels of AKT, pAKT and ABCG2 were normalized to those of GAPDH in the NCI-H460/MX20 cell lines. Values are the mean ± SD of 3 assays. Columns, mean; bars, SD; NS, not significant. B. Effect of Icotinib treatment on the subcellular localization of ABCG2 in NCI-H460/MX20 cell. ABCG2 staining is shown in green. DAPI (blue) counterstains the nuclei. C. Effect of Icotinib on the ATPase activity of ABCG2: The BeFx-sensitive specific ATPase activity of ABCG2 was determined in the presence of 0-5 μM of Icotinib as described in supplemental methods. The activity in the absence of Icotinib (basal activity) was considered to be 100%, and % -fold stimulation ± S.D. (Y-axis) was plotted as a function of indicated concentrations of Icotinib (X-axis). D. Effect of Icotinib on the photolabeling of ABCG2 with [125I]-IAAP: Crude membranes from ABCG2 expressing MCF7-FLV1000 cells were photo-crosslinked with [125I]-IAAP in the presence and absence of 0-50 μM of Icotinib as described in supplemental methods. [125I]-IAAP incorporated in ABCG2 band was quantified using ImageQuant software and plotted as % [125I]-IAAP incorporated ± S.D. (Y-axis) as a function of varying concentration of Icotinib (X-axis). The upper panel shows a representative autoradiogram from three independent experiments and the arrow represents the ABCG2 band photo-crosslinked with [125I]-IAAP. E. XP Glide predicted binding model of Icotinib with homology modeled ABCG2. The docked conformation of Icotinib as ball and stick model is shown within the large drug-binding cavity of ABCG2. Important amino acids are depicted as sticks with the atoms colored as carbon-green, hydrogen-white, nitrogen-blue, oxygen-red, whereas Icotinib is shown with the same color scheme as above except carbon atoms are represented in orange. Dotted black line indicates hydrogen bonding interactions, whereas dotted red line indicates electrostatic interactions. Left: ABCG2 is represented as Macromodel surface based on residue charge (hydrophobic-yellow, basic-blue). Middle: ABCG2 is represented as protein ribbons based on residue charge (hydrophobic-yellow, basic-blue, acidic-red). Right: Binding energies of Icotinib within each of the predicted binding sites of ABCG2. aSite grid generated using Arg482; bSite grid generated using Asn629; cSite grid generated using Arg383; dSite grid generated using Leu241 and Gly83.