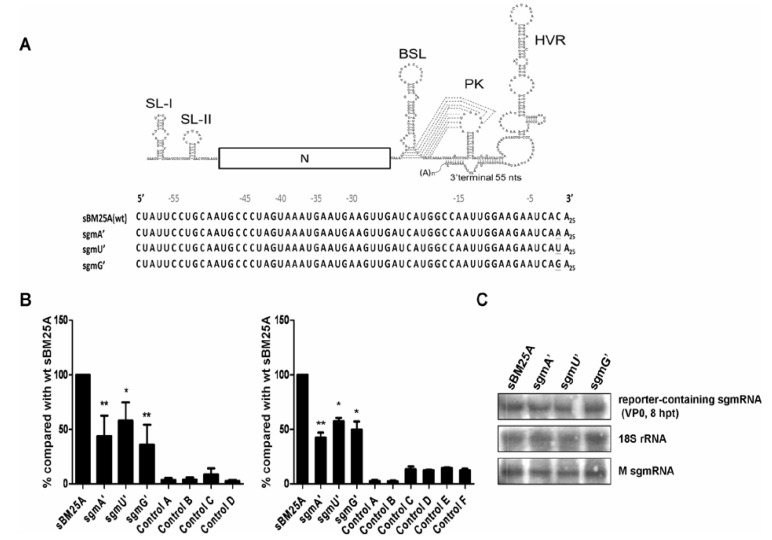
Figure 5.
The effect of the 3'-most nt species on the synthesis of (−)-strand sgmRNA. (A) Upper panel: schematic diagram depicting the sgmRNA. Lower panel: constructs with nucleotide substitution at the 3'-most nt of sgmRNA. (B) The relative efficiency of (−)-strand RNA synthesis between the constructs, as measured by RT-qPCR with (left panel) or without (right panel) head-to-tail ligation. Left panel: Control A: total cellular RNA from mock-infected cells. Control B: total cellular RNA from BCoV-infected cells. Control C: total cellular RNA from sBM25A-transfected mock-infected cells. Control D: a mixture of BCoV-infected cellular RNA extracted at 8 hpt and sBM25A transcript. Right panel: Control A: total cellular RNA from mock-infected cells. Control B: total cellular RNA from BCoV-infected cells. Control C: total cellular RNA from sBM25A-transfected mock-infected cells. Control D: total cellular RNA from sgmA’-transfected mock-infected cells. Control E: total cellular RNA from sgmU’-transfected mock-infected cells. Control F: total cellular RNA from sgmG’-transfected mock-infected cells. (C) Measurements of reporter-containing sgmRNA, 18S rRNA and M sgmRNA (from helper virus) at 8 hpt of VP0 by Northern analysis. Values (B) represent the mean ± SD of three individual experiment s. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.