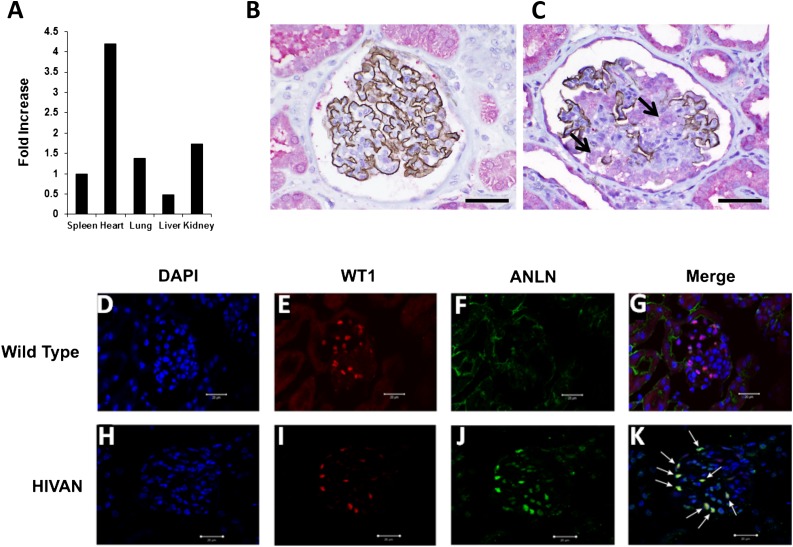
Figure 2.
Anillin expression in human and murine FSGS. (A) Real-time PCR is used to assess anillin mRNA expression in different organs. Anillin is ubiquitously expressed in all organs, including the kidney. All values are normalized for expression in the spleen. (B) Normal kidney biopsy tissue is double stained for synaptopodin with anti-human mouse mAb with brown DAB chromogen and anillin anti-human rabbit polyclonal antibody with Fast Red stain. Synaptopodin is strongly expressed in the glomerulus and the podocyte and the expression of anillin is mainly in the tubules. (C) Double staining for synaptopodin and anillin in a glomerulus with FSGS shows patchy expression of synaptopodin in the glomerulus and significant upregulation of anillin expression in the glomerulus and the reactive podocyte (black arrow) compared with normal kidney tissue. (D–G) The middle panel shows double immunostaining for WT1 (red) and anillin (green) in wild-type mice, and DAPI (blue) for nuclear staining. WT1 is expressed in the glomerulus mainly in the nucleus with little or no anillin expression. (I–K) In the lower panel, kidney tissues from HIVAN VPR mice showed reduced expression of WT1 (I), upregulation of anillin in the glomerulus (J), and colocalization of anillin with WT1 (white arrows in K). DAB, diaminobenzidine; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Original magnification, ×400 in B and C; ×40 in D–K. Scale bars in B and C represent a distance of 50 microns; scale bars in D–K represent a distance of 20 microns.