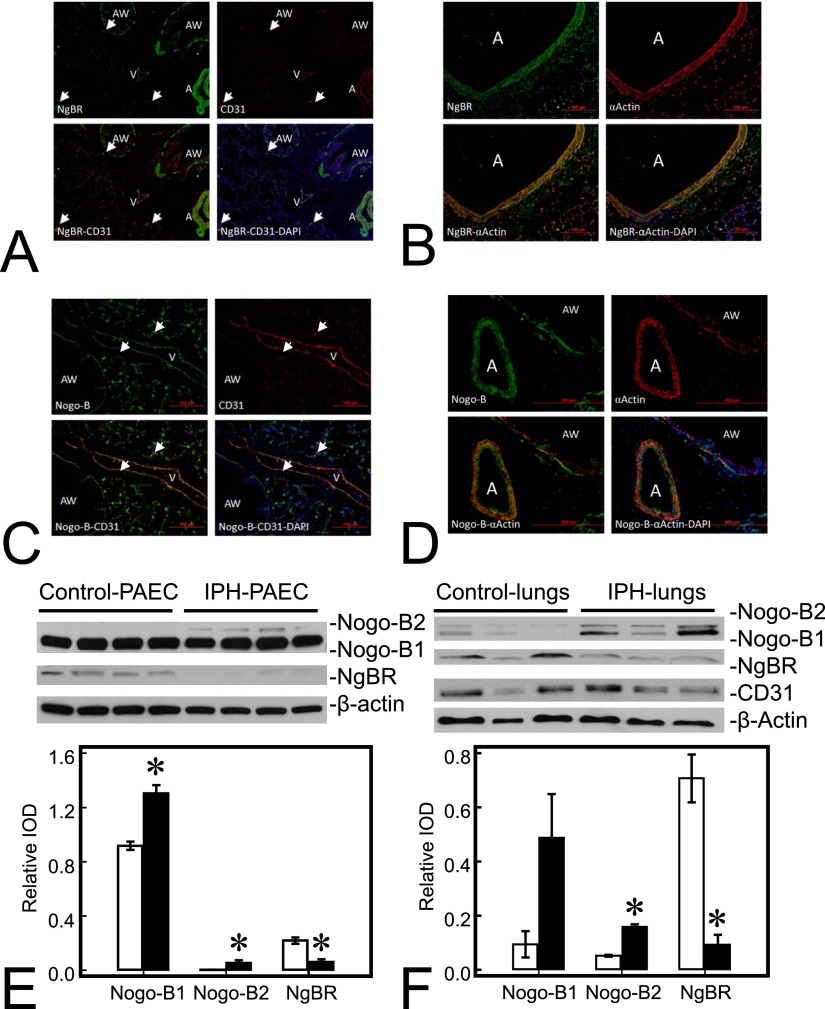
Figure 1.
Nogo-B receptor (NgBR) and its ligand, Nogo-B (NgB), are widely distributed in fetal sheep lungs. (A) NgBR (green) is detected in airway (AW), artery (A), and vein (V) in lung sections; CD31 (red) staining is in the endothelial lining of pulmonary vessels (A and V); colocalization of NgBR and CD31 (yellow) is observed in the lining of A and V, indicating endothelial localization of NgBR. (B) NgBR (green) and smooth muscle α-actin (red) colocalize (yellow) in the muscular layer of A, indicating smooth muscle location of NgBR. (C) Nogo-B (green) is also widely distributed in the lung, including A, V, pneumocytes, and AW, and colocalizes (yellow) with CD31 (red) of a vein in this section. (D) Nogo-B is also distributed in smooth muscle cells (red) of A and AW. Nogo-B level is increased, whereas NgBR level is decreased in pulmonary artery endothelial cells (PAECs) and lungs from lambs with intrauterine pulmonary hypertension (IPH). (E) Levels of both Nogo-B1 and Nogo-B2, subisoforms of Nogo-B, are increased in IPH PAECs (1.42-fold and 14.8-fold for Nogo-B1 and Nogo-B2, respectively) compared with control PAECs. The level of NgBR decreased by roughly 72% in IPH-PAECs compared with control PAECs. (F) Similar to PAECs, levels of Nogo-B1and Nogo-B2 were also increased in IPH lungs (5.44-fold and 2.98-fold for Nogo-B1 and Nogo-B2, respectively), whereas the level of NgBR was decreased by roughly 87%. The findings are similar when using CD31 as the loading control. Data are shown as mean (± SE). Open bar, control; closed bar, IPH; white arrow, microvasculature. *P < 0.05 compared with control PAECs or lungs. IOD, integrated optical density.