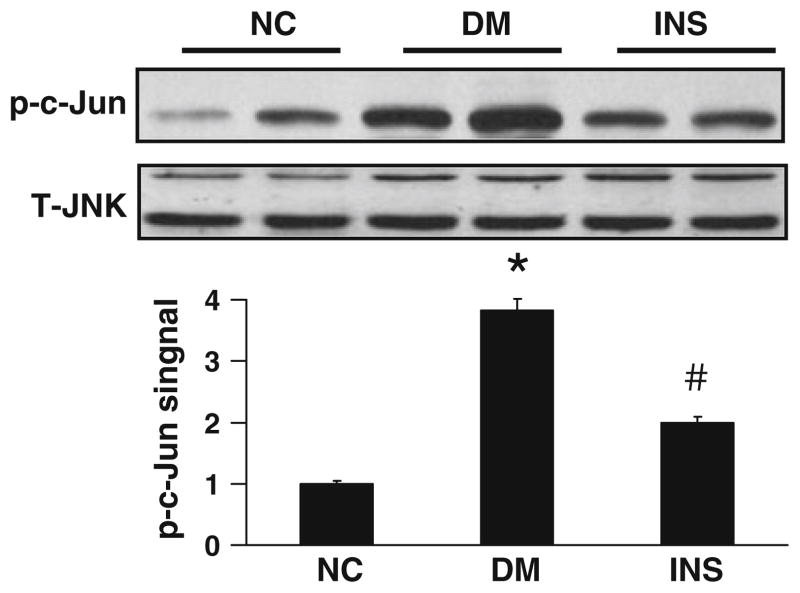
Fig. 2.
Insulin therapy reduced JNK activity in the liver of diabetic rats. JNK activity was determined by phosphorylation status of its substrate c-JUN in a Western blot. To normalize for JNK activity, JNK proteins were examined in cell lysates. Anti-JNK antibody that detects both JNK1 and JNK2 was used. The relative signal levels were determined by densitometry. Each bar represents the mean ± SD (n = 4–6). *P < 0.05 vs. NC; #P < 0.05 vs. DM. NC normal control rats; DM diabetic rats with no therapy; INS diabetic rats treated with insulin