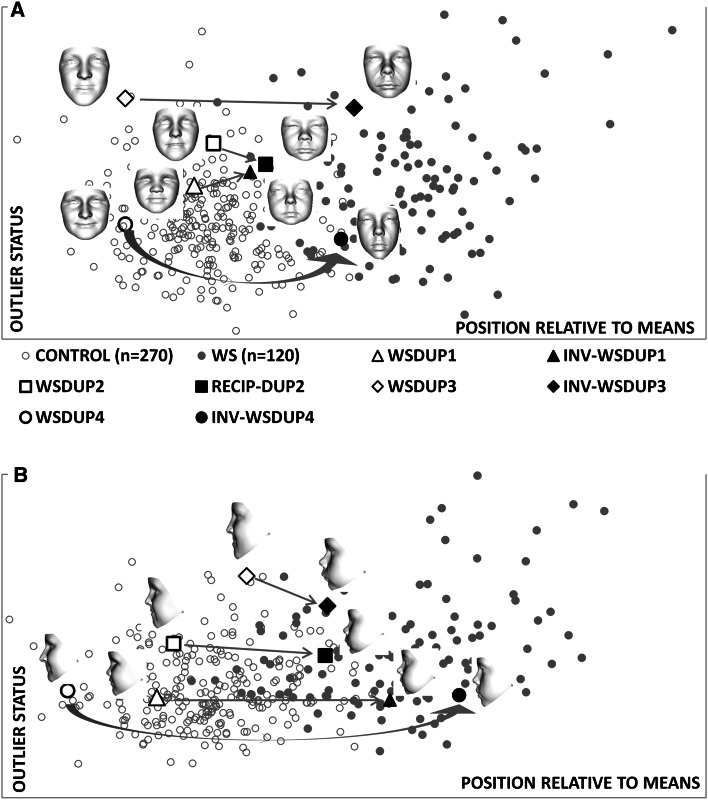
Fig. 3.
Closest mean classification of inversions of dup7q11.23 cases. The arrows emphasise position change in closest mean classification for the faces of the duplication cases in Fig. 1 f–h and their normative inversions. The horizontal axis determines relative similarity to the mean of the control group compared to the mean of the affected group. The vertical axis reflects the outlier status in terms of distance from the hyperline linking the means of the two groups under comparison. In a, the inversions of two duplication cases are classified at the periphery of the Williams–Beuren syndrome cluster. A third duplication inverts to well within the Williams–Beuren syndrome cluster. In b, when only the curvilinear mid-line facial profile is considered, all inversions are within the Williams–Beuren syndrome cluster. This is consistent with clinical evaluation suggesting the inverted faces to be somewhat wider than the typical Williams-Beuren syndrome facies but very Williams–Beuren syndrome-like in nose, lips and mid-line profile