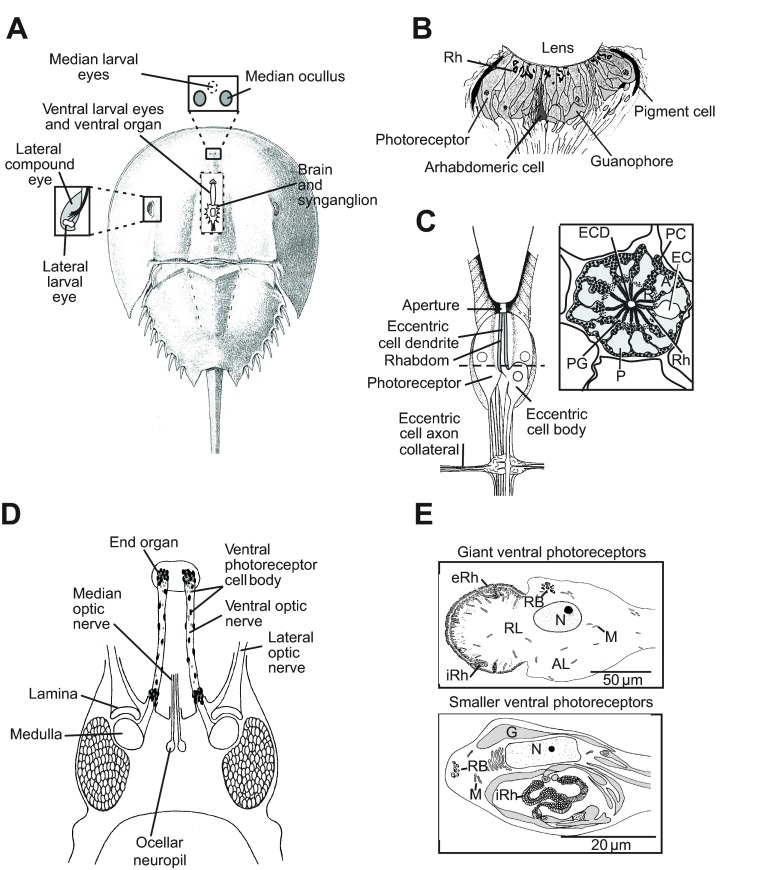
Fig. 1.
The Limulus polyphemus visual system. (A) Schematic of a dorsal view of L. polyphemus showing the positions of its eyes. Box on the left: enlargement of the lateral compound eye to show the location of the lateral larval eye. Box above: location of the median larval eyes (MEs) beneath the carapace between the two median ocelli. Cutaway in the center: locations of the brain, synganglion (circumesophageal ring) and ventral larval eyes, which end beneath the ventral organ. (B) Schematic of a longitudinal section through a median ocellus. Rhabdoms (Rh) of ME photoreceptors are located in a layer close to the lens (modified from Jones et al., 1971). (C) Left: schematic of a longitudinal section through a lateral eye ommatidium. Right: schematic of a cross-section of a lateral eye ommatidium at the level of the dashed line on the left. (D) Schematic of a dorsal view of the brain and ventral optic nerves. The locations of the optic ganglia (lamina and medulla) and the ocellar neuropil are indicated. The dark ovals scattered along the optic nerves and clustered at the end organ and near the brain represent cell bodies of the giant and smaller ventral photoreceptors. (E) Diagrams of ventral photoreceptors. Top: giant ventral photoreceptors. Bottom: one of two types of smaller ventral photoreceptors. The type shown has an extensive internal rhabdom. A second type of smaller ventral photoreceptor has an external rhabdom and is organized much like the giant ventral photoreceptors. A, arhabdomeral segment; AL, arhabdomeral lobe; EC, eccentric cell body; ECD, eccentric cell dendrite; eRh, external rhabdom; G, glia; iRh, internal rhabdom; M, mitochondria; N, nucleus; P, photoreceptor cell; PC, pigment cell; PG, photoreceptor pigment granules; R, rhabdomeral segment; RL, rhabdomeral lobe; RB, residual bodies.