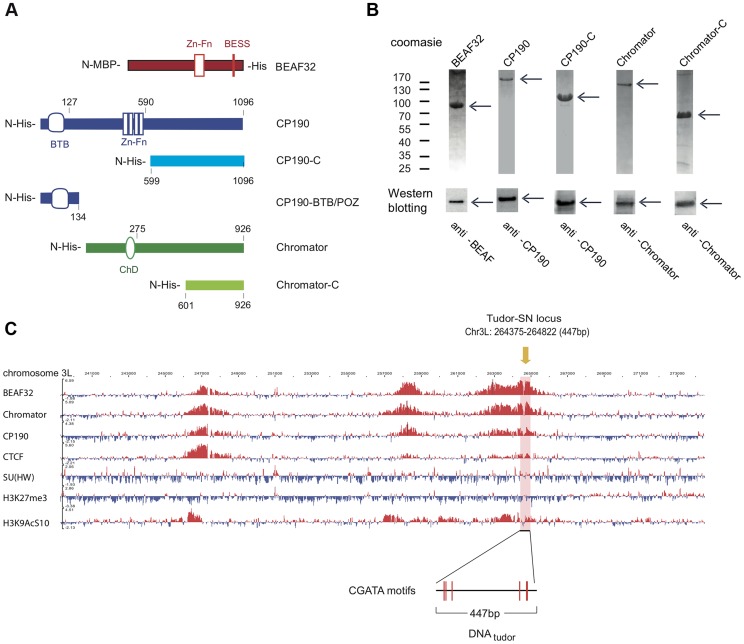
Figure 1. Protein constructs, protein purification, and genomic localization of insulator proteins and associated factors.
(A) Description of protein constructs used in this study. C2H2 zinc-finger motifs (Zn-Fn) are shown as vertical rectangles, BESS motifs as a vertical red line, BTB/POZ domains as rounded boxes and chromo-domains (ChD) as ellipses. N-terminal domains (N-) are always on left. Lengths of each domain or fragment is indicated in number of amino-acids from the N-terminal end. His indicates a 6-Histidine tag, and MBP the maltose binding-protein. (B) Purity of purified BEAF32, CP190, CP190-C, Chromator, and Chromator-C was assessed by poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE, Coomassie blue staining, top panel), and resulted in single bands (>95% purity, see arrows). Molecular weight ladder is shown on the left. Western-blot analysis (bottom panel) of each purified protein shows the specific recognition by each of the antibodies developed. (C) Binding profile of insulator-associated proteins (BEAF32, Chromator, CP190, dCTCF, Su(HW)) and epigenetic marks (H4K27m3, and H3K9AcS10) in chromosome 3L from ModEncode data (S2 cells; Generic Genome Browser version 2.40). Tracks used are described in Supplementary Table S6. For each protein, the track depicts the MAT score of each probe plotted on the y-axis versus chromosomal position plotted along the x-axis. The genomic region used for EMSA-analysis (DNAtudor, part of the Tudor-SN lucus) is highlighted in pink (3L: 264375–264822). DNAtudor contains six CGATA binding motifs.