Figure 10. Patterns of electrostatic similarity in the S2 specificity pockets of cathepsin B, cathepsin L, and papain.
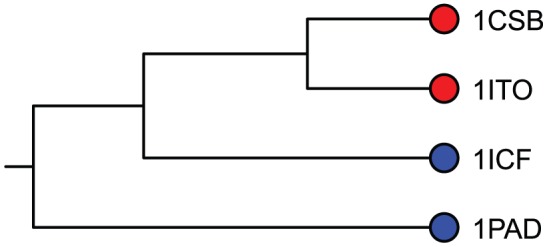
The color coding, which is independent of tree topology, indicates the types of P2 residue preferred by each protein. Cathepsin B's (red) prefer basic amino acids and cathepsin L and papain (blue) prefer large hydrophobic amino acids. The topology of the tree reflects patterns of similarity measured with different comparison algorithms. Proteins on adjacent branches have greater similarity than proteins on different subtrees. The topological separation of the cathepsin B's from cathepsin L and papain indicates that similarities and differences in the electrostatic character of S2 subsites, which create the differences in their binding preferences, were detected and correctly classified by VASP-E, using the Jaccard distance.
