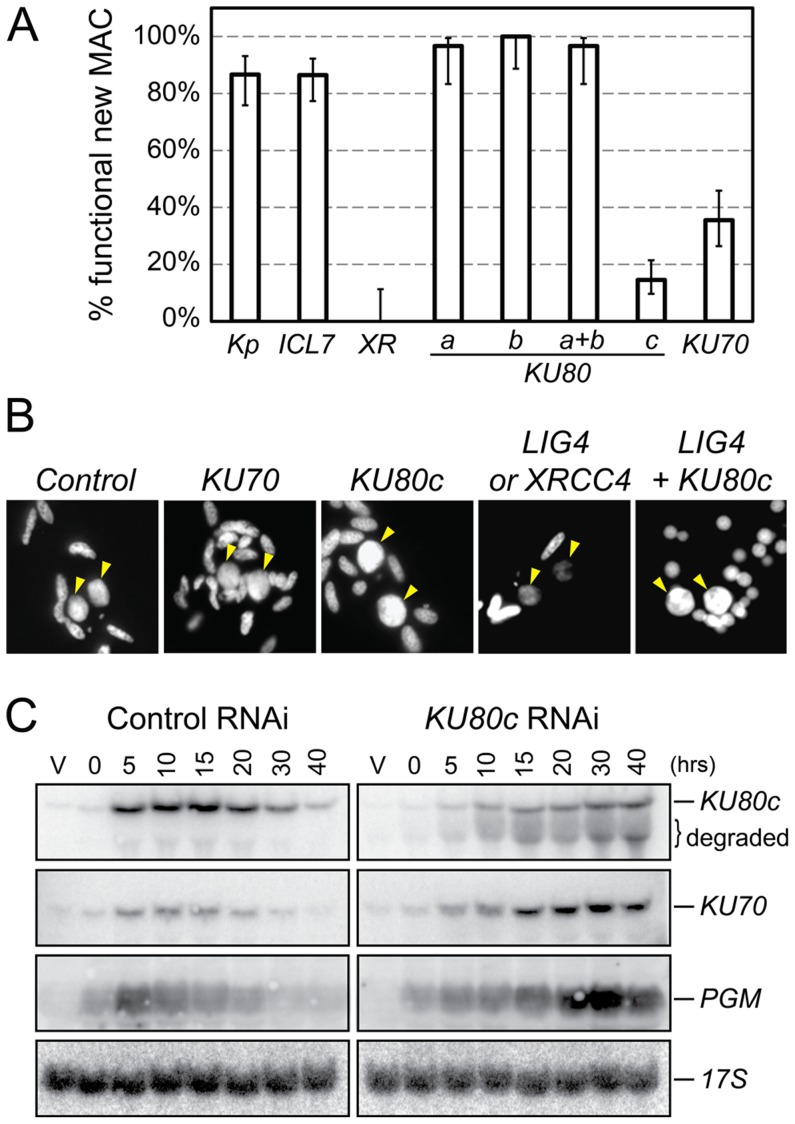
Figure 3. RNAi screen for essential KU genes during autogamy.
(A) Survival of the post-autogamous progeny of cells submitted to different combinations of RNAi. Kp: autogamy in standard K. pneumoniae medium; ICL7: RNAi against ICL7, a nonessential gene that encodes an infraciliary lattice centrin [47]; XR: RNAi against XRCC4. RNAi experiments against KU80 genes were performed using gene-specific inserts KU80-a2, KU80-b2 and KU80-c2 (see Figure S2). For each condition, 30 to ∼140 post-autogamous cells were analyzed. Each bar represents the percentage of viable post-autogamous cells carrying a functional new MAC, for each condition. Error bars represent the Wilson score intervals (95% confidence level), which are appropriate for a small number of trials or for values close to an extreme probability. (B) DAPI-staining of developing MACs during RNAi against ND7 (control), KU70, KU80c, XRCC4/LIG4 and LIG4 + KU80c. Developing MACs are indicated by yellow arrowheads. Upon LIG4 or XRCC4 RNAi, developing MACs exhibit faint DAPI staining, which correlates with a defect in DNA amplification [16]. (C) Northern blot hybridization of total RNA during a control time course experiment (ND7 RNAi) and in a KU80c RNAi. V: vegetative cells; T0: 60% of cells with fragmented MAC; other time-points refer to hours following T0 (Figure S1B).