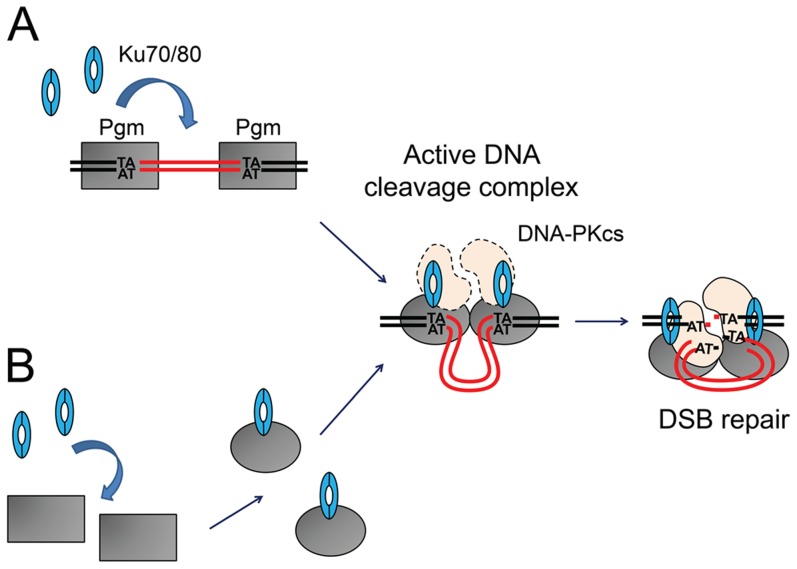
Figure 8. Models for the assembly of an active DNA cleavage complex.
(A) Ku associates with DNA-bound Pgm and activates DNA cleavage. Pgm and its putative partners (in grey) would recognize and bind the boundaries of eliminated sequences. The binding of Ku (in blue) activates Pgm for DNA cleavage (symbolized by the switch from a rectangular box to an oval), perhaps by assisting the formation of a synapse between both IES ends, in a transpososome-like intermediate. The DNA-PKcs catalytic subunit (in peach) may also be part of the active DNA cleavage complex. (B) Ku forms a complex with Pgm in the absence of DNA, activating the DNA binding and/or cleavage activities of Pgm. Following DNA cleavage, conformational remodeling of the complex would position Ku on broken DNA ends and allow it to perform its classical role in C-NHEJ-mediated DSB repair. MAC DNA is represented in black, IES DNA in red.