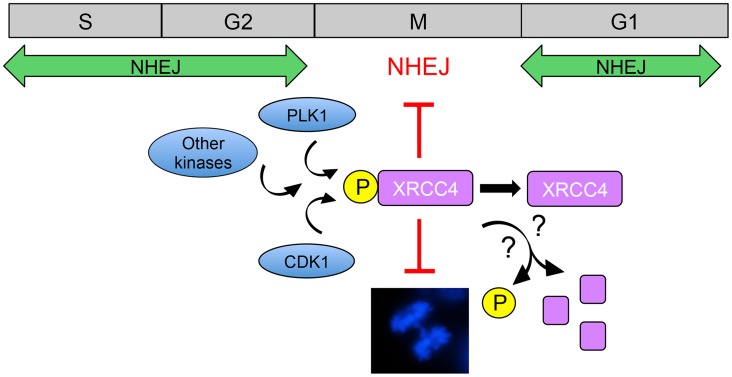
Figure 1. Model for suppression of NHEJ in mitosis by phosphorylated XRCC4.
NHEJ is the major pathway for the repair of radiation and topoisomerase II poison-induced DSBs in interphase mammalian cells. CDK1 and PLK1 are activated as cells enter mitosis and contribute to phosphorylation of XRCC4 on serine 326 in the unstructured, C-terminal tail [3]. It is also likely that other protein kinases are involved in phosphorylation of XRCC4 in mitosis. In ways that are yet to be determined, phosphorylated XRCC4 suppresses C-NHEJ in mitosis, preventing formation of anaphase bridges (shown in the DAPI-stained mitotic cell in the lower panel, from [22]). Serine 326 phosphorylation of XRCC4 in mitosis is transient [3], suggesting that phosphorylated XRCC4 is either dephosphorylated or degraded as cells exit mitosis, allowing C-NHEJ to resume in the subsequent G1 phase.