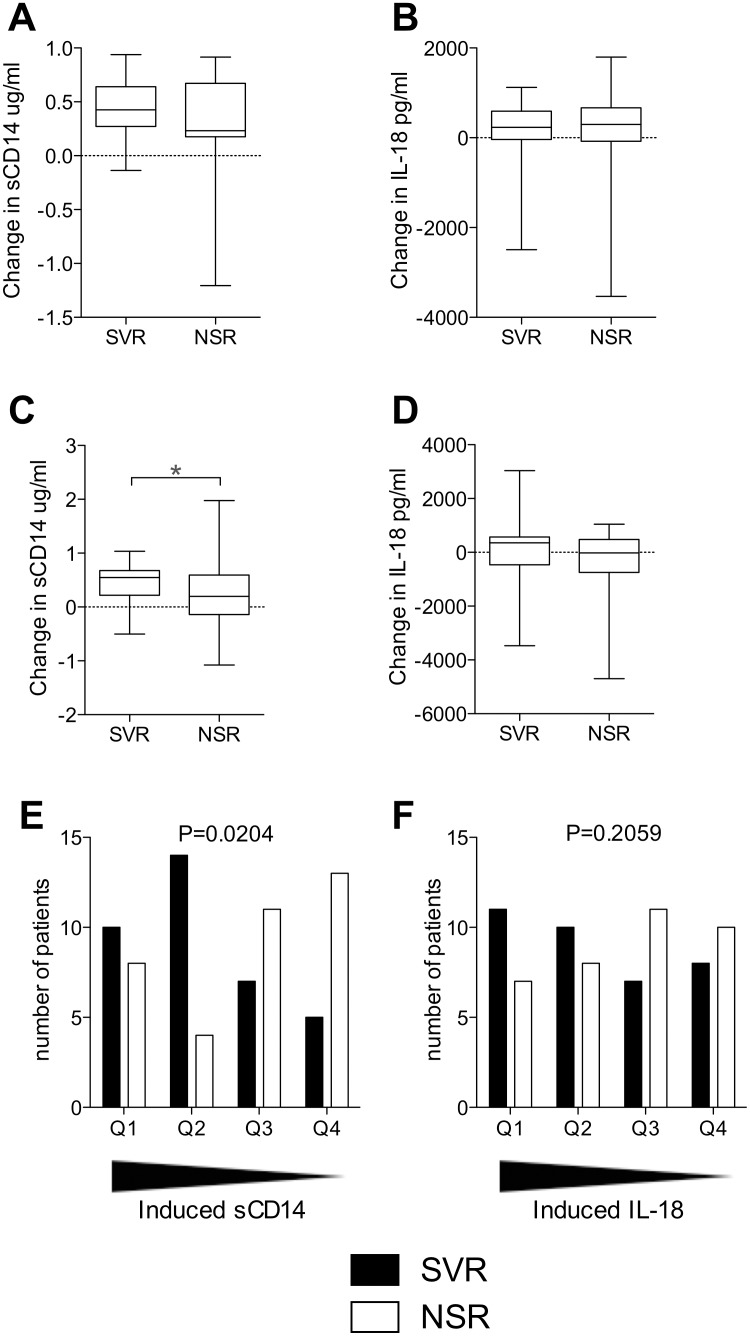
Figure 4. Induced elevation of sCD14 is associated with triple therapy outcome.
(A) Differences in the induction of sCD14 between sustained virological response (SVR) and no sustained response (NSR) patients whom undergo dual therapy (SVR n = 33, NSR n = 19). (B) Differences in the induction of IL-18 between SVR and NSR patients whom undergo dual therapy (SVR n = 33, NSR n = 19). (C) Differences in the induction of sCD14 between SVR and NSR patients whom undergo triple therapy (SVR n = 36, NSR n = 36, unpaired T test with Welch’s correction P = 0.0435). (D) Differences in the induction of IL-18 between SVR and NSR patients whom undergo triple therapy. *P≤0.05. Patients in the triple therapy cohort were ordered with those with the highest levels of sCD14 elevation in quartile 1 (Q1) to the lowest in Q4 and number of patients with a SVR or NSR in each quartile was assessed. (E) Number of SVR and NSR patients in each sCD14 quartile (n = 72). (F) Number of SVR and NSR patients in each IL-18 quartile (n = 72). P values shown represent Chi-squared test for trend.