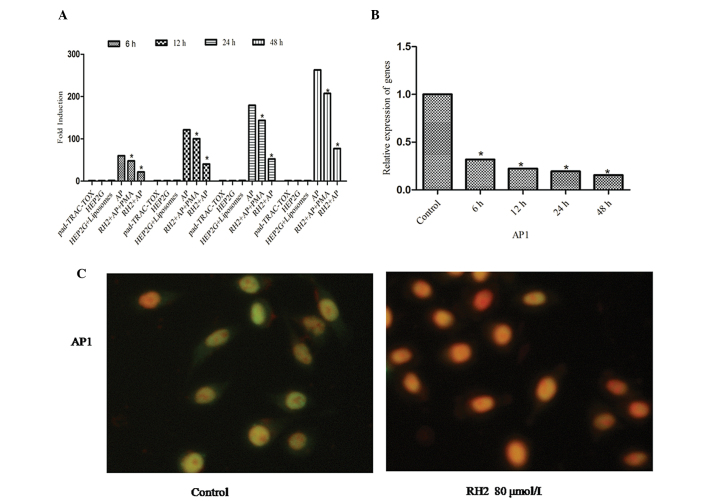
Figure 3.
AP-1 transcription factors were inhibited by ginsenoside Rh2 in HepG2 liver carcinoma cells. (A) Cells were transfected with either plasmid (pad-track-tox) as a positive control, left untreated as a negative control, transfected with liposomes as a false positive or transfected with plasmid encoding Renilla luciferase (pAP-1-luc) as the treated group. The treated group was divided into three subgroups, designated A1 (AP-1), B1 (AP-1+Rh2+PMA) and C1 (AP-1+Rh2). The B1 group was treated with 80 μM ginsenoside Rh2 and 30 μM PMA. The C1 group was treated with 80 μM Rh2 only. (B) HepG2 cells were incubated for 6, 12, 24 and 48 h with Rh2 (80 μM). The expression levels of AP-1 gene were measured by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. (C) Fluorescence microscopy images of AP-1 expression in isolated single cells (magnification, ×400). Results shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.*P<0.05 vs. control. AP-1, activator protein 1; PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate.