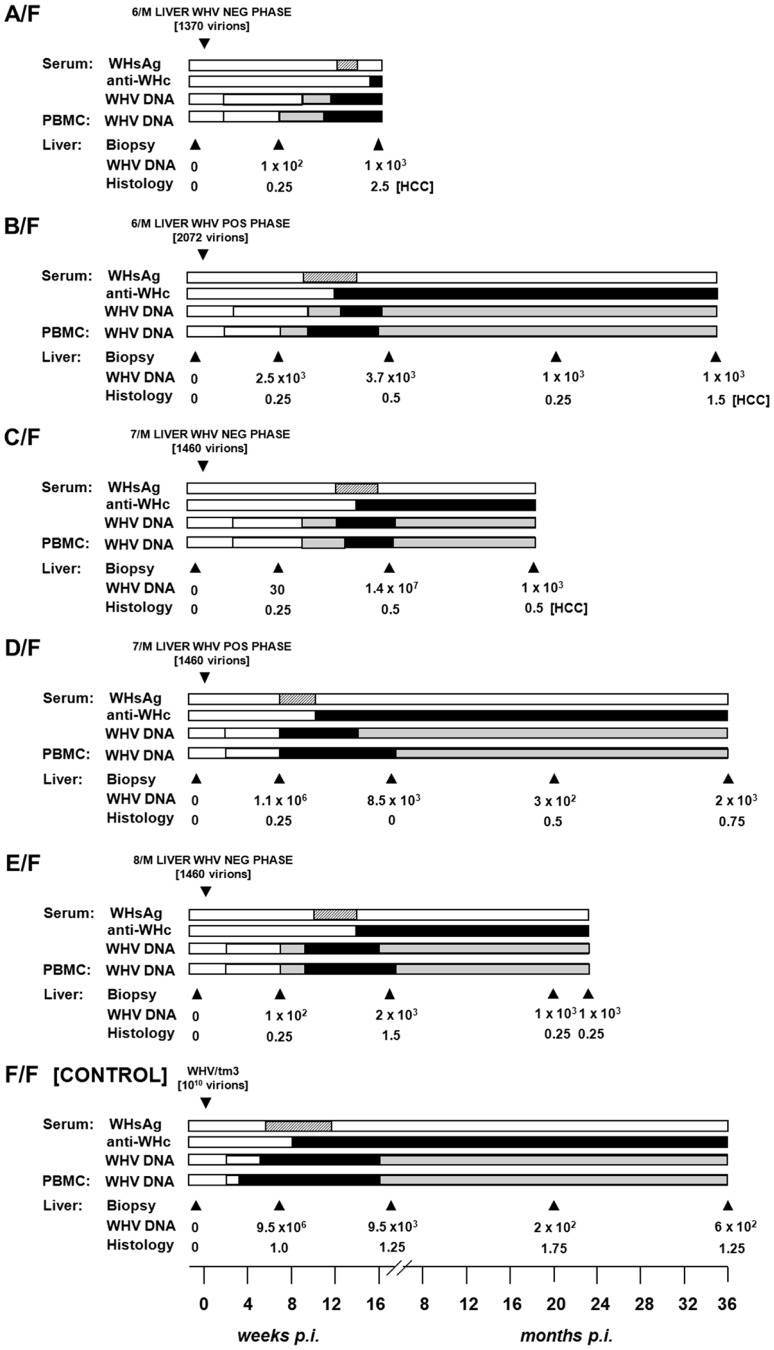
Figure 5. Serological profiles of WHV infection, detection of WHV DNA in sequential serum, PBMC and liver tissue samples, histological degree of hepatitis, and detection of HCC in initially healthy, WHV-naïve woodchucks inoculated with circulating WHV derived from the liver virus-negative and the liver virus-positive phases of POI.
Animals were i.v. injected with indicated amounts of WHV, presented in virus genome equivalents (vge), recovered by ultracentrifugation of pools of plasma and serum from the liver WHV-negative and the liver WHV-positive phases of POI from 6/M and 7/M, and from the liver WHV-negative phase of POI from 8/M woodchuck. A control F/F animal was injected with 1010 WHV/tm3 virions. The appearance and duration of serum WHsAg and anti-WHc positivity, the estimated WHV DNA loads in sera, PBMC and liver biopsy and autopsy samples, and liver morphological alterations were presented as indicated in the legend to Figure 1.