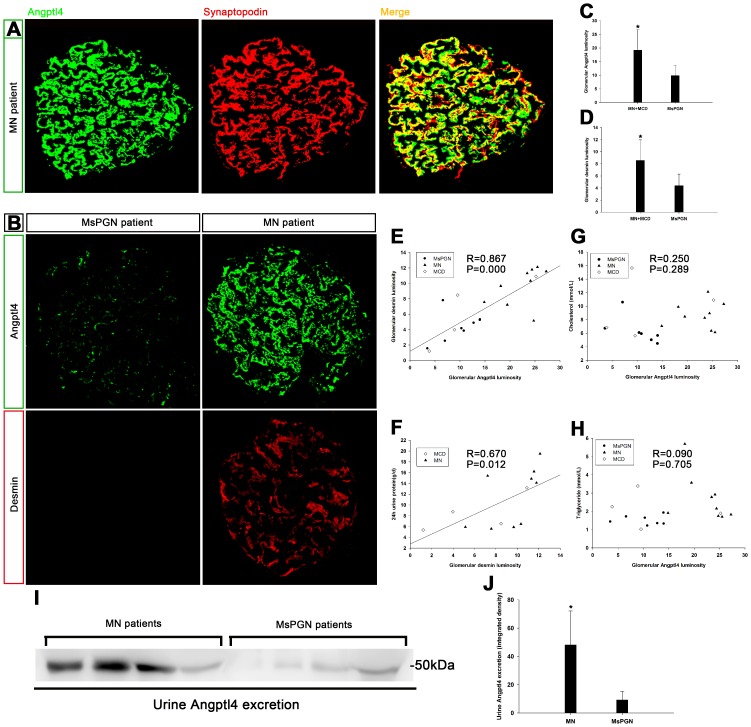
Figure 6. Expression of Angptl4 in human glomerulonephritis and its relationship with desmin and urine protein.
(A) Immunofluorescence of glomerular Angptl4 with synaptopodin in MN patients (magnification, x400). The overlap rate of Angptl4 and synaptopodin was 58.72%. (B) Immunofluorescence of glomerular Angptl4 and desmin in MN and MsPGN patients with similar nephrotic-range proteinuria (magnification, x400). Angptl4 and desmin expression levels were markedly upregulated in the MN patient compared with the MsPGN patient. (C and D) Quantification of the immunofluorescence intensities of glomerular Angptl4 and desmin in MN and MCD and non-podocytopathy (MsPGN). *P<0.01 vs. MsPGN. The expression levels of Angptl4 and desmin were notably increased in MN and MCD patients relative to MsPGN patients. (E) Scatter diagram of Angptl4 and desmin in 20 patients. A correlative analysis revealed positive correlations between glomerular Angptl4 and desmin expression. (F) Scatter diagram of desmin and urine protein in podocytopathy patients (13 patients). Correlative analysis revealed positive correlations between desmin and proteinuria. (G and H) The scatter diagrams reveal the relationships between Angptl4, cholesterol, and triglycerides in 20 patients. There were no correlations between glomerular Angptl4 expression and cholesterol or between Angptl4 and triglycerides. (I) Western blot analysis of urine Angptl4 excretion in MN and MsPGN patients with similar nephrotic-range proteinuria. (J) Quantification of the western blot analysis of urine Angptl4 excretion in MN and MsPGN patients. *P<0.05 vs. MsPGN. Urine Angptl4 excretion was more obvious in MN patients than in MsPGN patients.