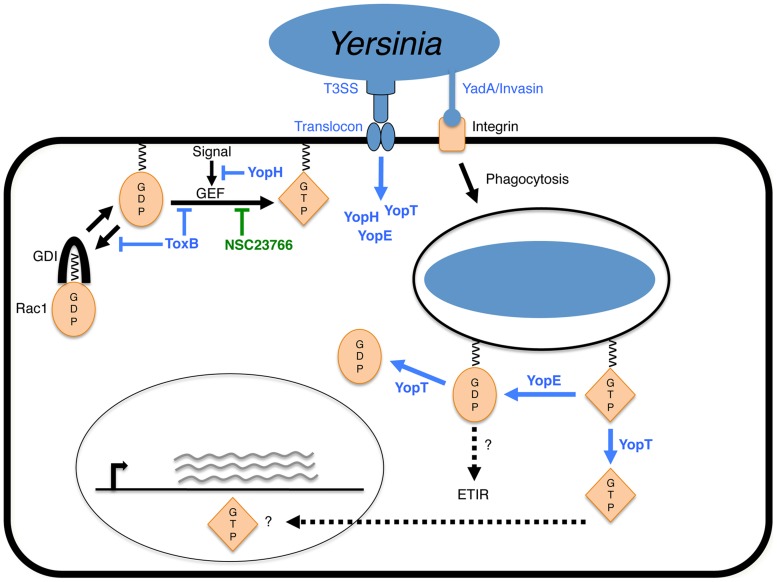
Figure 10. Model of YopE-triggered killing of Yersinia in macrophages.
Binding of Y. pseudotuberculosis to macrophage β1 integrin via YadA or Invasin allows for translocation of Yop effectors by the type III secretion system (T3SS) and initiates phagocytosis. Regulation of Rac1 activation by host guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI) or guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) is shown at the plasma membrane. For simplicity, inhibition of Rac1 activation by YopH, Toxin B or NSC23766 is shown at the plasma membrane and manipulation of Rac1 by YopE and YopT is shown on phagosomal membrane. Production of membrane-localized inactive Rac1-GDP is proposed to generate an effector-triggered immune response (ETIR), resulting in increased killing of Yersinia in phagosomes. YopT counteracts the ETIR by releasing GDP-bound Rac1 from the membrane. Additionally, activated GTP-bound Rac1 released from the membrane by YopT has been shown to localize to the nucleus and may activate gene expression.